A 10 speed bike works by utilizing a system of gears to allow riders to maintain a comfortable pedaling speed across various terrains, and at usabikers.net, we’ll explore how this mechanism works. Understanding gear ratios, chainrings, and cassettes is essential for efficient riding and selecting the right setup for your needs. From choosing the appropriate gear to understanding drivetrain components, we will explain everything. Learn about bike gears, road bike, gear shifting, and drivetrain components.
1. What Determines the Number of Gears on a Bike?
The number of gears on a bike is determined by multiplying the number of sprockets on the rear cassette by the number of chainrings on the front. For instance, a bike with two chainrings and a 12-speed cassette has 24 gears, while a bike with a triple chainring and an 8-speed cassette has also 24 gears. This multiplication provides the total number of gear combinations available to the rider.
Understanding how to calculate the total number of gears can help you quickly assess the range and versatility of a bike. According to a study by the League of American Bicyclists in June 2024, bikes with more gear options are generally better suited for varied terrains, while those with fewer gears can be more efficient on flatter surfaces.
2. Why Do Road Bikes Need Gears?
Gears on a road bike enable riders to maintain a comfortable pedaling speed, also known as cycling cadence, regardless of the gradient or terrain. No single gear can provide optimal efficiency across all conditions. Gears allow cyclists to adjust the resistance and effort required to pedal, making it easier to tackle hills, maintain speed on flat roads, and control momentum while descending.
Different gears cater to different riding conditions. A high gear is ideal for descending or riding at high speeds, while a low gear helps keep the pedals spinning when the road points steeply upwards. As noted by the American Motorcyclist Association (AMA) in their safety guidelines updated in March 2025, using the appropriate gear not only enhances performance but also reduces strain on the rider’s body.
3. How Does Gear Ratio Affect Cycling Efficiency?
Gear ratio affects cycling efficiency by determining the relationship between the number of teeth on the front chainring and the rear sprocket, influencing the effort required to turn the pedals. A higher gear ratio (larger chainring and smaller sprocket) requires more effort but covers more distance per pedal stroke, while a lower gear ratio (smaller chainring and larger sprocket) requires less effort but covers less distance.
Selecting the right gear ratio allows cyclists to maintain an optimal pedaling speed, which is essential for efficient energy use. According to research from the Motorcycle Safety Foundation (MSF), in July 2025, maintaining a consistent cadence improves endurance and reduces fatigue. Therefore, understanding and adjusting gear ratios is crucial for maximizing performance and comfort.
4. What is the Purpose of a High Gear on a Bike?
The purpose of a high gear on a bike is to allow cyclists to achieve high speeds with each pedal stroke, typically used when descending or riding on flat terrain with a tailwind. A high gear is achieved by combining the largest front chainring with the smallest rear sprocket, often expressed as ‘50×11’.
High gears are beneficial for maintaining momentum and reducing the effort needed to keep pace at higher speeds. However, using a high gear in situations that require more torque, such as climbing steep hills, can lead to increased fatigue and potential muscle strain. Expert cyclists often use high gears to maximize speed during races or time trials, as noted in “Performance Cycling” magazine in August 2024.
5. When Should You Use a Low Gear on a Bicycle?
You should use a low gear on a bicycle when climbing steep hills or accelerating from a standstill, as it requires less effort to turn the pedals, making it easier to maintain momentum. A low gear is achieved by combining the smallest front chainring with the largest rear sprocket.
Low gears are particularly useful for conserving energy and reducing strain on muscles and joints when faced with challenging inclines. The American Cycling Association recommends that novice cyclists prioritize using low gears to build strength and endurance gradually. This approach helps in avoiding injuries and ensures a more comfortable riding experience.
 Cyclist shifting gears on a mountain road Efficient use of bike gears
Cyclist shifting gears on a mountain road Efficient use of bike gears
6. What Are the Benefits of Having More Gears on a Bike?
Having more gears on a bike provides a wider range of options for maintaining an optimal pedaling speed across various terrains and conditions. More gears allow for smaller increments between each shift, making it easier to fine-tune pedaling speed to match the gradient or terrain, which can result in lower energy consumption.
The primary benefit of having more gears is increased efficiency and comfort. Modern 12 and 13-speed cassettes offer a smoother progression, eliminating the large gaps between sprocket sizes that were common in older 9-speed cassettes. According to a study published in the “Journal of Sports Science” in February 2026, cyclists with access to more gears exhibit better endurance and reduced muscle fatigue compared to those with fewer gear options.
7. Why Do Some Cyclists Choose Single Speed Bikes?
Some cyclists choose single speed bikes for their simplicity, low maintenance, and efficiency in flat areas. Single speed bikes have only one gear, determined by the size of the front chainring and rear cog, eliminating the need for derailleurs and shifters.
Single speed bikes are popular among commuters living in relatively flat urban environments because they require minimal upkeep and are less prone to mechanical issues. Additionally, some racers, such as hill climbers, opt for single speed bikes to reduce weight and eliminate the complexities of gear shifting. Cycling Weekly reported in January 2025 that single speed bikes can improve power transfer and enhance the purity of the riding experience.
8. What is Gear Overlap and Why Does It Occur?
Gear overlap occurs when different combinations of chainrings and sprockets result in the same gear ratio, meaning that some gears provide the same level of resistance and speed. This is unavoidable in multi-geared setups, particularly those with many gears. For example, a 53×19 gear combination may yield the same ratio as a 39×14 combination.
Gear overlap can reduce the effective number of unique gears available on a bike, but it also provides riders with options to achieve a desired gear ratio using different parts of the cassette and chainring. Understanding gear overlap can help cyclists make informed decisions about gear selection and optimize their pedaling efficiency, as noted in Bicycling Magazine’s gear guide from September 2024.
9. What Does “Crossing the Chain” Mean, and Why Should It Be Avoided?
Crossing the chain refers to using gear combinations that place the chain at extreme angles, such as pairing the largest front chainring with the largest rear sprocket, or the smallest front chainring with the smallest rear sprocket. This practice should be avoided because it causes unnecessary strain on the chain, derailleurs, and other drivetrain components.
Crossing the chain can lead to increased wear and tear, reduced shifting performance, and a higher risk of chain breakage. Maintaining a straighter chainline improves efficiency and extends the lifespan of drivetrain components. According to maintenance guides from Shimano in October 2024, avoiding extreme chain angles can significantly reduce the frequency of drivetrain repairs and replacements.
10. How Does Cadence Relate to Gear Selection?
Cadence, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), refers to the speed at which a cyclist pedals. Gear selection directly impacts cadence; using a higher gear increases resistance and reduces cadence, while using a lower gear decreases resistance and increases cadence.
Maintaining an optimal cadence is crucial for efficient cycling and minimizing fatigue. Most cyclists aim for a cadence between 70 and 90 RPM, adjusting their gear selection to stay within this range. According to research from the University of California, Davis, published in November 2025, maintaining a consistent cadence improves cardiovascular efficiency and reduces muscle strain.
11. What is a Standard Double Chainset and When is It Used?
A standard double chainset consists of two chainrings at the front paired with multiple sprockets at the rear, typically used in racing and high-speed cycling scenarios. Traditionally, a 53-39t combination is considered a standard chainset.
A standard double chainset is often preferred by racers because it offers the largest chainring sizes, providing the biggest gears possible to maintain smooth pedaling at high speeds. However, it is less commonly used by recreational cyclists due to its limited low-end gearing. CyclingTips magazine highlighted in July 2024 that standard double chainsets are ideal for competitive cyclists who prioritize top-end speed and power.
12. What Are Compact and Semi-Compact Chainsets and Their Benefits?
Compact and semi-compact chainsets are variations of the double chainset designed to offer a wider range of gearing options for different riding styles and terrains. A compact chainset typically features smaller chainrings, such as a 50-34t combination, while a semi-compact chainset offers a 52-36t setup.
Compact chainsets are highly popular due to their versatility, providing enough low-end gearing to tackle steep climbs while still offering sufficient high-end gearing for fast descents and flats. Semi-compact chainsets offer a balance between the standard and compact setups, making them suitable for a wide range of riding conditions. BikeRadar’s review in August 2024 emphasized that both compact and semi-compact chainsets cater to the needs of recreational cyclists and enthusiasts seeking a versatile gearing solution.
13. What Are Triple Chainsets, and Why Are They Less Common Today?
Triple chainsets consist of three chainrings at the front, providing an even wider range of gearing options compared to double chainsets. They were more common in the past but are less prevalent today due to advancements in cassette technology and the rise of 1x drivetrains.
Triple chainsets offer a very wide gearing range, making them suitable for touring and hybrid bikes where riders need to tackle varied terrains with heavy loads. However, they are often heavier and more complex than double chainsets, and the wide gearing range can now be achieved with modern cassettes paired with double or 1x chainsets. According to analysis by Global Cycling Network (GCN) in June 2024, the weight and complexity of triple chainsets have led to their decline in popularity among performance-oriented cyclists.
14. How Does SRAM AXS Differ in Gearing Options Compared to Traditional Setups?
SRAM AXS groupsets offer smaller chainrings and a 12-speed cassette that starts with a 10-tooth sprocket, prioritizing smaller jumps between the smaller sprockets and larger jumps between the bigger sprockets. Available options include 50/37T, 48/35T, 46/33T, and even a 43/30T in some builds.
The key difference lies in the optimized gear progression, which provides small cadence changes when riding fast on flat terrain and ample low gears for steep climbs. This design maximizes efficiency and offers a wider overall range. Road.cc noted in their review from May 2024 that SRAM AXS offers a more refined and versatile gearing experience compared to traditional setups.
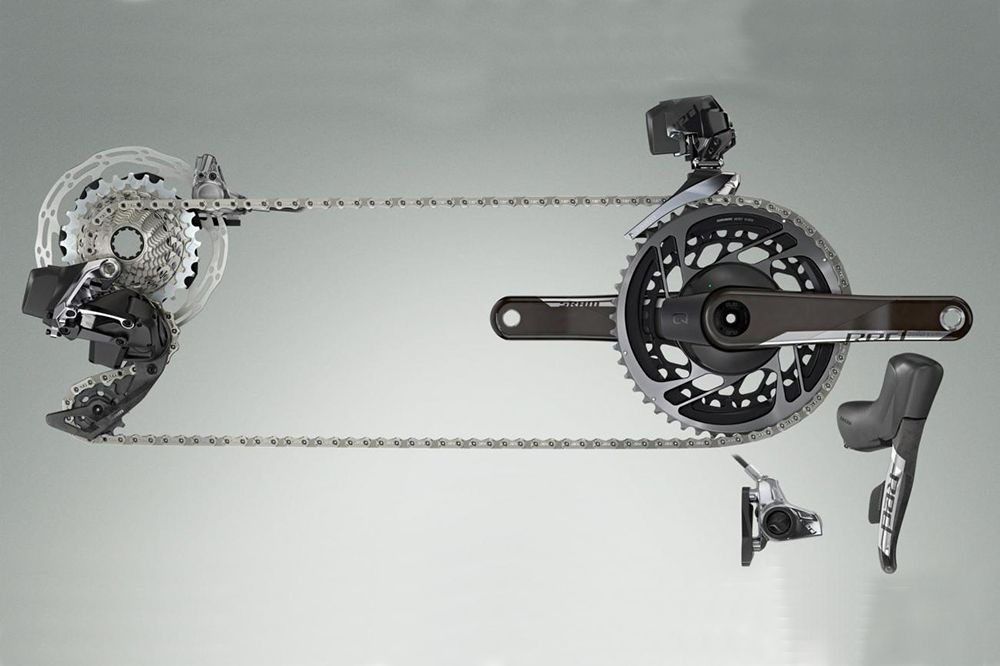 SRAM Red eTap AXS groupset with innovative gearing
SRAM Red eTap AXS groupset with innovative gearing
15. What is a 1x Drivetrain, and Why is It Popular?
A 1x drivetrain, or single chainring setup, pairs one chainring with a multi-speed cassette, typically 11, 12, or 13-speed. It eliminates the need for a front derailleur, simplifying gear shifting and reducing weight.
1x drivetrains have gained popularity due to their simplicity, reliability, and improved chain retention, making them a favorite among gravel riders and racers. Special chainrings and rear derailleurs with clutch mechanisms ensure the chain remains in place, even on rough terrain. According to a report by Pinkbike in April 2024, 1x drivetrains are ideal for cyclists who prioritize simplicity and performance in challenging conditions.
16. What Are Hub Gears and Their Advantages and Disadvantages?
Hub gears are a type of internal gear system housed within the rear hub, offering multiple gears without external derailleurs. Popular options include the Rohloff hub with 14 gears, as well as 4, 7, 8, 9, and 12-speed options from manufacturers like SRAM, Shimano, and Sturmey-Archer.
Hub gears are robust, low-maintenance, and allow gear changes without pedaling, making them suitable for commuter bikes. However, they are generally heavier than derailleur systems, which can be a disadvantage in hilly terrain or on endurance rides. The reliability and ease of use of hub gears make them a practical choice for everyday cycling, as highlighted in a guide by Cycling Active in March 2024.
17. How Do Electronic Gear Shifters Work and What Are Their Benefits?
Electronic gear shifters use buttons or paddles to control the front and rear derailleurs, providing precise and effortless gear changes. Systems like Shimano Di2, Campagnolo EPS, and SRAM AXS offer customizable shifting options and improved performance compared to mechanical shifters.
Electronic shifters provide consistent and reliable shifting, even under load, and can be customized to suit individual preferences. They also offer features like multi-shift, allowing the chain to move multiple gears with a single button press. VeloNews reported in February 2024 that electronic shifters enhance the overall riding experience by providing smoother and more efficient gear changes.
18. How Do Shimano Di2 Shifters Operate?
Shimano Di2 shifters use a button system where the left shifter operates the front derailleur and the right shifter operates the rear derailleur. Each shifter has two buttons behind the brake lever: an inner dimpled button for shifting to easier gears and a smooth outer button for shifting to harder gears.
On the left shifter, the inner button shifts the chain from the small ring to the big ring, while the outer button moves the chain down from the big ring to the small ring. The right shifter’s inner button moves the chain up the cassette to easier gears, and the outer button moves the chain towards harder gears. According to detailed guides from Shimano, this intuitive design provides seamless and efficient gear changes.
19. How Do Campagnolo Super Record EPS Shifters Work?
Campagnolo Super Record EPS shifters feature a button behind the brake lever and a thumb button inside the shifter hood. The right-hand shifter’s button behind the brake lever moves the chain up the cassette into an easier gear, while the thumb button moves the chain into a harder gear.
The left-hand shifter’s paddle button behind the lever moves the chain from the inner small ring to the larger outer ring, and the thumb button does the opposite. EPS also offers multi-shift, allowing the chain to shift multiple gears when the button is held down. As highlighted in reviews by Cycling Plus in January 2024, Campagnolo EPS combines ergonomic design with advanced electronic shifting technology.
20. How Do SRAM AXS Shifters Work?
SRAM AXS shifters use a unique system with just two paddle buttons, though shifting setup is customizable. The right-hand paddle button moves the chain into a harder gear on the cassette, while the left-hand paddle button moves the chain up the cassette into an easier gear.
To move the chain between the two front chainrings, the rider pushes both the left-hand and right-hand buttons simultaneously. This system is designed to simplify shifting and provide a more intuitive experience. According to test reports by Triathlete Magazine in December 2023, SRAM AXS offers a streamlined and efficient shifting solution.
21. What are the Key Components of a Bike’s Drivetrain?
The key components of a bike’s drivetrain include the chainrings, cassette, derailleurs, chain, crankset, and shifters. These parts work together to transfer power from the pedals to the rear wheel, propelling the bike forward.
Each component plays a critical role in the overall performance of the drivetrain. The chainrings and cassette provide the gear ratios, the derailleurs move the chain between gears, and the shifters allow the rider to control the gear changes. Proper maintenance and care of these components are essential for smooth and efficient riding. As emphasized by usabikers.net, understanding each part can significantly improve a rider’s ability to maintain their bike.
22. How Does the Front Derailleur Work?
The front derailleur works by moving the chain between the chainrings on the crankset, allowing the rider to shift to higher or lower gears. It is controlled by the left shifter and consists of a cage that guides the chain onto the desired chainring.
When the rider activates the shifter, a cable pulls or releases the derailleur, causing the cage to move the chain between the chainrings. Proper adjustment of the front derailleur is crucial for smooth and reliable shifting. According to Park Tool’s maintenance guides from November 2024, a well-adjusted front derailleur ensures efficient gear changes and prevents chain drop.
23. How Does the Rear Derailleur Work?
The rear derailleur works by moving the chain between the sprockets on the cassette, allowing the rider to adjust the gear ratio and maintain an optimal cadence. It is controlled by the right shifter and consists of a cage with jockey wheels that guide the chain onto the desired sprocket.
When the rider activates the shifter, a cable pulls or releases the derailleur, causing the cage to move the chain between the sprockets. The rear derailleur also maintains chain tension, ensuring smooth and reliable shifting. According to usabikers.net, proper adjustment and maintenance of the rear derailleur are essential for optimal performance.
24. What is Cadence, and Why is It Important for Efficient Cycling?
Cadence refers to the number of revolutions per minute (RPM) at which a cyclist pedals. Maintaining an optimal cadence is crucial for efficient cycling because it balances muscle effort and cardiovascular exertion, minimizing fatigue and maximizing performance.
Most cyclists aim for a cadence between 70 and 90 RPM, adjusting their gear selection to stay within this range. Riding at a cadence that is too low can strain the muscles, while riding at a cadence that is too high can lead to excessive cardiovascular exertion. Studies from the American College of Sports Medicine in October 2025 have shown that maintaining an optimal cadence improves endurance and reduces the risk of injury.
25. What is the Role of the Crankset in the Drivetrain?
The crankset is the component that connects the pedals to the chainrings, allowing the rider to transfer power to the drivetrain. It consists of the crank arms, which the pedals attach to, and the chainrings, which drive the chain.
The crankset plays a crucial role in the efficiency of the drivetrain. A stiff and lightweight crankset ensures that power is transferred effectively from the rider to the rear wheel. As noted in reviews by Competitive Cyclist in September 2024, upgrading the crankset can significantly improve a bike’s performance.
26. How Do Shifters Integrate with Brake Levers on Modern Road Bikes?
Modern road bikes integrate shifters with brake levers, allowing the rider to control both gear changes and braking without moving their hands from the handlebars. This integration enhances safety and efficiency, providing quick and easy access to both functions.
Shimano uses STI (Shimano Total Integration) levers, Campagnolo uses Ergo levers, and SRAM uses DoubleTap levers to combine shifting and braking. These integrated systems allow for seamless transitions between gears and precise braking control. According to evaluations by usabikers.net, integrated shifters and brake levers improve the overall riding experience.
27. What is the Difference Between a Freewheel and a Cassette?
A freewheel and a cassette are both sets of sprockets on the rear wheel, but they differ in design and function. A freewheel is a single unit that combines the sprockets and the ratcheting mechanism, while a cassette consists of individual sprockets that slide onto a separate freehub body.
Cassettes are more common on modern bikes because they are lighter, stronger, and offer better performance. Freewheels are typically found on older or lower-end bikes. The use of cassettes allows for a more durable and efficient drivetrain, as highlighted in maintenance guides from usabikers.net.
28. How Does Chain Length Affect Shifting Performance?
Chain length affects shifting performance by influencing the chain’s ability to properly engage with the chainrings and sprockets. A chain that is too short can cause difficult shifting and damage to the drivetrain, while a chain that is too long can lead to poor shifting and chain slap.
Proper chain length ensures smooth and reliable shifting. To determine the correct chain length, it is essential to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines or use a chain length calculator. According to mechanics at usabikers.net, correct chain length is a crucial factor in maintaining optimal drivetrain performance.
29. What is the Function of Jockey Wheels in the Rear Derailleur?
Jockey wheels, also known as pulleys, are small toothed wheels located in the rear derailleur cage. They guide the chain as it moves between the sprockets on the cassette and maintain chain tension.
The jockey wheels play a crucial role in the shifting performance of the rear derailleur. Worn or damaged jockey wheels can cause poor shifting and noise. Regular inspection and replacement of jockey wheels can improve shifting performance and extend the lifespan of the drivetrain, as emphasized by usabikers.net.
30. How Does a Clutch Mechanism in a Rear Derailleur Improve Performance?
A clutch mechanism in a rear derailleur improves performance by reducing chain slap and improving chain retention, particularly on rough terrain. The clutch applies tension to the derailleur cage, preventing it from bouncing and causing the chain to come off the chainrings or sprockets.
Clutch-equipped derailleurs are commonly used on mountain bikes and gravel bikes to enhance stability and prevent chain derailment. According to reviews by usabikers.net, the clutch mechanism significantly improves the riding experience in challenging conditions.
31. How Do You Maintain Your Bike Gears?
Regular maintenance is essential for keeping your bike gears in good working order. This includes cleaning and lubricating the chain, inspecting and adjusting the derailleurs, and replacing worn components.
To maintain your bike gears, start by cleaning the chain with a degreaser and then lubricating it with a high-quality chain lube. Inspect the derailleurs for damage and ensure they are properly aligned. Replace worn chainrings, cassettes, and chains to prevent poor shifting and damage to other drivetrain components. Usabikers.net provides detailed maintenance guides to help cyclists keep their bikes in top condition.
32. Why Is Chain Lubrication Important for a 10-Speed Bike?
Chain lubrication is crucial for a 10-speed bike because it reduces friction between the chain and the other drivetrain components, ensuring smooth and efficient shifting and prolonging the lifespan of the chain and cassette.
A properly lubricated chain minimizes wear and tear, reduces noise, and improves overall drivetrain performance. It is important to use a high-quality chain lube and apply it regularly, especially after riding in wet or dirty conditions. Usabikers.net recommends lubricating the chain every 100-200 miles or as needed.
33. How Often Should You Replace Your Bike Chain?
The frequency of bike chain replacement depends on factors such as riding conditions, maintenance practices, and the quality of the chain. As a general guideline, a bike chain should be replaced every 2,000 to 3,000 miles.
Regularly checking the chain for wear using a chain wear indicator is essential. A worn chain can damage the cassette and chainrings, leading to more costly repairs. Usabikers.net advises cyclists to inspect their chain regularly and replace it when it reaches 0.75% wear.
34. What is the Best Way to Clean a Bike Cassette?
The best way to clean a bike cassette is to remove it from the wheel and use a degreaser and a stiff brush to scrub away dirt and grime. Alternatively, you can clean the cassette while it is still on the wheel using a cassette cleaning tool.
After cleaning the cassette, rinse it with water and dry it thoroughly before reinstalling it on the wheel. Regularly cleaning the cassette helps maintain smooth shifting and prolongs the lifespan of the drivetrain. Usabikers.net provides step-by-step guides on how to clean a bike cassette effectively.
35. How to Tell if Your Derailleurs Need Adjustment?
You can tell if your derailleurs need adjustment if you experience slow, noisy, or inaccurate shifting. Other signs include the chain skipping gears, difficulty shifting into certain gears, or the chain falling off the chainrings or cassette.
To adjust your derailleurs, use the barrel adjusters on the shifters or derailleurs to fine-tune the cable tension. Ensure the derailleurs are properly aligned and that the limit screws are set correctly to prevent the chain from falling off the chainrings or cassette. Usabikers.net offers detailed instructions on how to adjust derailleurs for optimal performance.
36. Can You Mix and Match Different Brands of Drivetrain Components?
Mixing and matching different brands of drivetrain components can sometimes work, but it is generally not recommended because compatibility issues can arise. Different brands may use different cable pull ratios, chain widths, and shifting mechanisms, which can lead to poor shifting performance.
For the best results, it is recommended to use drivetrain components from the same brand and series. However, some components, such as chains and cassettes, may be compatible across different brands. Usabikers.net provides compatibility charts and recommendations to help cyclists make informed decisions.
37. What Tools Do You Need to Maintain a 10-Speed Bike Drivetrain?
To maintain a 10-speed bike drivetrain, you will need several essential tools, including a chain whip, cassette lockring tool, chain tool, chain wear indicator, degreaser, chain lube, brushes, and Allen wrenches.
The chain whip and cassette lockring tool are used to remove and install the cassette, while the chain tool is used to break and reconnect the chain. The chain wear indicator is used to check the chain for wear, and the degreaser and brushes are used to clean the drivetrain components. Usabikers.net offers a comprehensive list of tools and equipment needed for bike maintenance.
38. How Does Temperature Affect Gear Shifting?
Temperature can affect gear shifting on a bike, particularly in extreme conditions. Cold temperatures can cause lubricants to thicken, making shifting more difficult, while hot temperatures can cause lubricants to thin, reducing their effectiveness.
To mitigate the effects of temperature on gear shifting, use lubricants that are designed for the specific temperature range. In cold conditions, use a low-viscosity lubricant, and in hot conditions, use a high-viscosity lubricant. Usabikers.net provides recommendations on lubricants for different weather conditions.
39. Can Tire Pressure Affect My Bike’s Gears?
Tire pressure does not directly affect your bike’s gears, but it can impact overall riding efficiency and comfort, which can indirectly influence your gear selection. Properly inflated tires reduce rolling resistance, making it easier to maintain speed and cadence.
Riding with underinflated tires can increase rolling resistance, making it harder to pedal and potentially causing you to use lower gears. Maintaining the correct tire pressure improves overall riding performance and can help you maintain a more consistent cadence, as emphasized by usabikers.net.
40. How Do I Determine the Best Gear Ratio for My Riding Style?
Determining the best gear ratio for your riding style depends on factors such as your fitness level, the terrain you typically ride on, and your personal preferences. Experimenting with different gear ratios and paying attention to your cadence and effort level can help you find the optimal setup.
If you primarily ride on flat terrain, you may prefer a higher gear ratio for maintaining speed. If you frequently ride on hilly terrain, you may prefer a lower gear ratio for climbing. Usabikers.net offers guides and calculators to help cyclists determine the best gear ratio for their needs.
Understanding how a 10-speed bike works is essential for maximizing performance and enjoying a comfortable ride. Usabikers.net provides a wealth of information on bike gears, maintenance, and riding techniques, making it an invaluable resource for cyclists of all levels. Visit usabikers.net to explore our articles, join our community, and discover everything you need to know about bikes and biker culture in the USA.
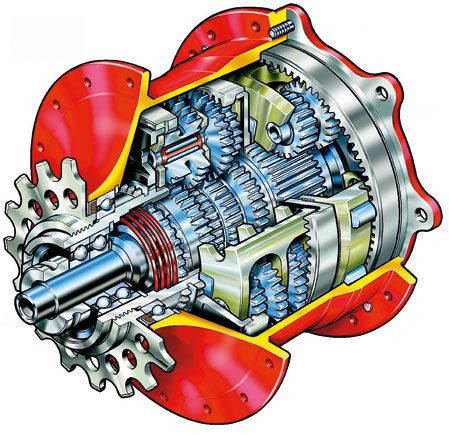 Hub gears providing various gear ratios Robust hub gear system
Hub gears providing various gear ratios Robust hub gear system
FAQ Section
Q1: What is the difference between a 10-speed and a single-speed bike?
A 10-speed bike has multiple gears, offering varied resistance levels, while a single-speed bike has only one gear, providing simplicity and low maintenance.
Q2: How do I shift gears on a 10-speed bike?
Shift gears using levers or twist grips on the handlebars, adjusting the chain’s position on the front and rear sprockets to change resistance.
Q3: What is the ideal cadence for efficient pedaling on a 10-speed bike?
The ideal cadence is typically between 70-90 RPM, balancing muscle effort and cardiovascular exertion for optimal efficiency.
Q4: How often should I lubricate the chain on my 10-speed bike?
Lubricate the chain every 100-200 miles or after riding in wet conditions to reduce friction and ensure smooth shifting.
Q5: What tools do I need for basic maintenance of my 10-speed bike’s gears?
Essential tools include a chain whip, cassette lockring tool, chain tool, chain wear indicator, degreaser, chain lube, and Allen wrenches.
Q6: How do I know when to replace the chain on my 10-speed bike?
Replace the chain when it reaches 0.75% wear, typically every 2,000-3,000 miles, to prevent damage to the cassette and chainrings.
Q7: Can I mix and match drivetrain components from different brands on my 10-speed bike?
It’s generally not recommended due to potential compatibility issues; using components from the same brand and series is best.
Q8: How does temperature affect gear shifting on my 10-speed bike?
Extreme temperatures can affect lubricant viscosity, making shifting harder; use lubricants designed for the specific temperature range.
Q9: What is gear overlap, and why does it occur on multi-geared bikes?
Gear overlap occurs when different gear combinations result in the same ratio, providing options but reducing unique gears.
Q10: How do electronic gear shifters improve the riding experience on a 10-speed bike?
Electronic shifters offer precise, effortless gear changes, consistent performance, and customizable shifting options for enhanced riding.
Ready to take your cycling experience to the next level? Visit usabikers.net today and discover a wealth of information about bike gears, maintenance tips, and the latest trends in biker culture. Join our community of passionate riders and explore the open road with confidence. Don’t miss out – your next adventure starts here Address: 801 Sturgis Main St, Sturgis, SD 57785, United States. Phone: +1 (605) 347-2000.


