Choosing the right bike frame size is crucial for comfort, efficiency, and overall riding enjoyment. Whether you’re buying your first bike, upgrading to a new one, or renting a bicycle for a ride, understanding how bike frame size is measured ensures you get the perfect fit. Different manufacturers may have varying sizing conventions, which makes knowing the fundamental frame measurements essential for accurate comparisons.
This guide from usabikers.net will walk you through the key measurements that define a bike frame, whether you’re interested in road bikes or mountain bikes. By understanding these measurements, you’ll be better equipped to choose a bike that fits you perfectly and suits your riding style. We’ll cover everything from top tube length to bottom bracket drop, providing clear instructions and insights into why each measurement matters.
For a deeper dive into how these measurements impact handling, you might also want to explore our comprehensive guide to mountain bike geometry. While focused on mountain bikes, many of the principles discussed apply to road bikes as well.
We also offer specific advice on selecting the right size frame for road bikes and mountain bikes, and dedicated guidance for choosing women’s bikes.
Key Bike Geometry Measurements Explained
Before we delve into the “how-to” of measuring your bike frame, let’s define the essential bike geometry measurements you need to know:
- Top Tube Length (Effective): This is the horizontal distance between the center of the head tube and the center of the seat post. It’s a critical measurement for reach and overall bike fit.
- Seat Tube Length: Measured from the center of the bottom bracket to the top of the seat tube, this affects standover height and available seatpost adjustment.
- Reach: The horizontal distance from the center of the bottom bracket to the top center of the head tube. Reach is a key factor in determining the bike’s cockpit length and rider position.
- Stack: The vertical distance from the center of the bottom bracket to the top center of the head tube. Stack height influences handlebar height and rider posture.
- Wheelbase: The distance between the front and rear wheel axles. Wheelbase affects stability and handling characteristics.
- Chainstay Length: The distance from the center of the bottom bracket to the rear axle. Chainstay length impacts the bike’s responsiveness and climbing ability.
- Front Center: The distance from the center of the bottom bracket to the front axle. Front center influences weight distribution and handling.
- Seat Tube Angle: The angle of the seat tube relative to the horizontal plane. Seat tube angle affects hip angle and pedaling efficiency.
- Head Tube Angle: The angle of the head tube relative to the horizontal plane. Head tube angle influences steering responsiveness and stability.
- Bottom Bracket Drop: The vertical distance the bottom bracket is below the wheel axles. Bottom bracket drop affects stability and cornering ability.
- Bottom Bracket Height: The vertical distance from the ground to the center of the bottom bracket. Bottom bracket height affects ground clearance and center of gravity.
Tools You’ll Need to Measure Your Bike Frame
To accurately measure your bike frame and understand its dimensions, you will need these tools:
- Tape Measure: Essential for measuring linear distances in centimeters or millimeters for precision.
- Clinometer: Used to measure angles. Smartphone apps are readily available for this purpose, making angle measurement accessible.
- Spirit Level (or Straight Edge with Clinometer App): A long spirit level ensures horizontal and vertical measurements are accurate. Alternatively, a straight piece of wood combined with a clinometer app can serve the same purpose.
- Plumb Line (or String and Weight): A plumb line helps establish a vertical reference. You can improvise with a string and a small weight like a blob of Blu Tack or a washer.
While metric units (centimeters and millimeters) are the standard in bike frame measurement, especially for newer bikes, some manufacturers, particularly for mountain bikes, might still use inches. For consistency and ease of comparison, we recommend using metric units throughout the measuring process. If needed, you can convert centimeters to inches by dividing by 2.54.
It’s also worth noting that most bike manufacturers provide detailed geometry charts for their current models on their websites. If your bike is a recent model, checking the manufacturer’s geometry chart is highly recommended as it offers precise measurements and can be a valuable reference.
Step-by-Step Guide: Measuring Top Tube Length
 Measuring top tube length on a bicycle frame
Measuring top tube length on a bicycle frame
Alt text: How to measure effective top tube length on a bike frame, showing tape measure positioned horizontally from head tube to seat post.
The effective top tube length or virtual top tube length is a crucial measurement, especially on bikes with sloping top tubes, which are very common nowadays. While some geometry charts might list the actual top tube length, the effective top tube length provides a standardized horizontal measurement, regardless of the top tube’s angle.
To measure the effective top tube length:
- Identify the center of your head tube and the center of your seat post.
- Use your spirit level or clinometer app to ensure you are measuring a perfectly horizontal line.
- Measure the horizontal distance from the center of the head tube to the center of the seat post. This measurement is your effective top tube length.
Many road bike manufacturers use top tube length as a primary sizing metric. However, mountain bikes and some road bikes often use sizing designations like S, M, L, etc. It’s important to remember that these size designations can vary significantly between brands. For example, a size S frame from one brand might have a top tube length equivalent to a size M from another.
Also, be aware that different brands may use slightly different methods for measuring virtual top tube length. Colnago, for example, measures to a vertical projection from the top of the seat tube, resulting in slightly shorter measurements compared to brands that account for seat post setback. Always consider these nuances when comparing bike geometry charts.
Step-by-Step Guide: Measuring Seat Tube Length
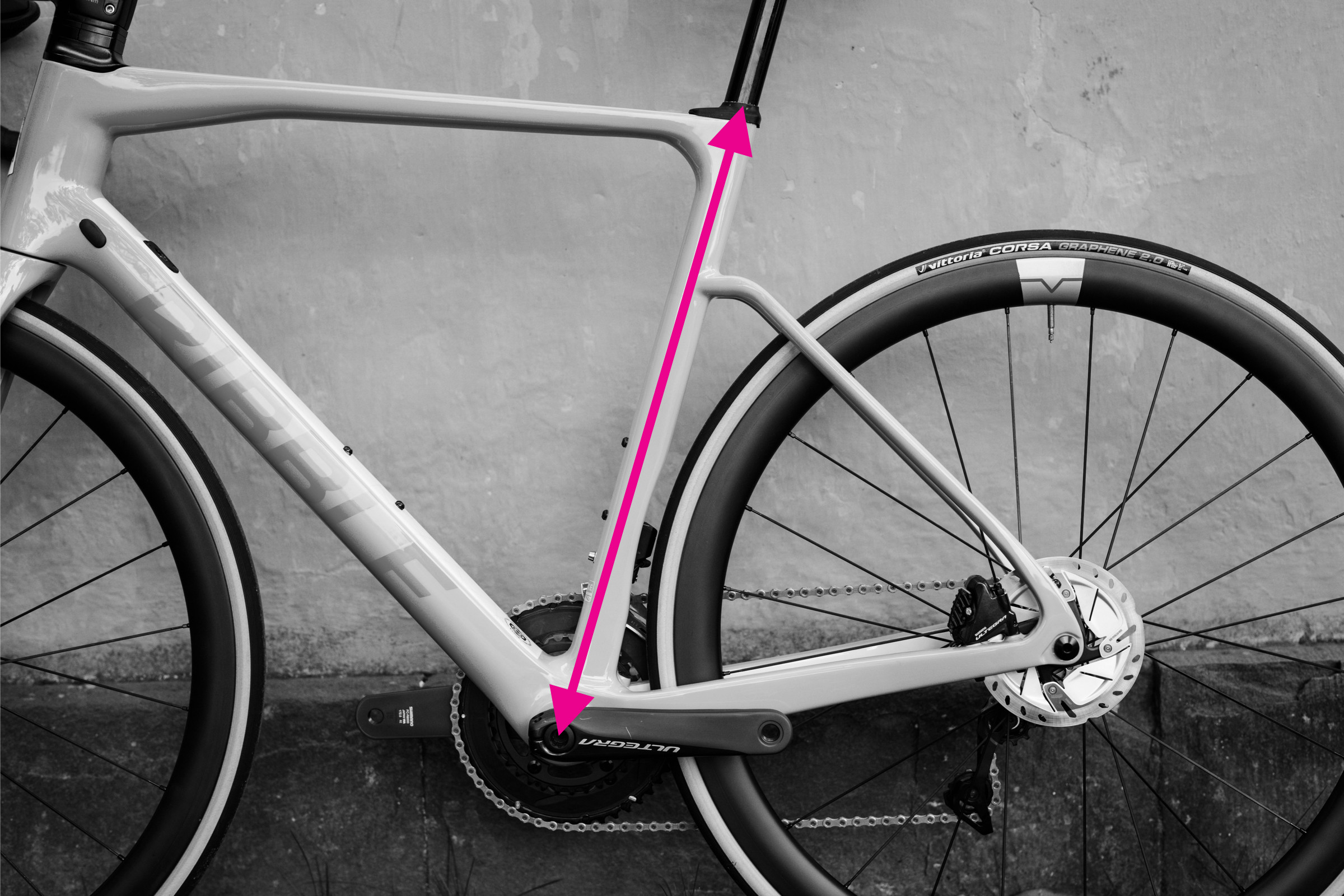 Measuring seat tube length on a bicycle frame
Measuring seat tube length on a bicycle frame
Alt text: Measuring seat tube length on a bicycle frame with a tape measure from bottom bracket center to top of seat tube.
Seat tube length is measured as a straight line from the center of the bottom bracket to the top of the seat tube. While seemingly straightforward, certain frame designs can make this measurement less clear-cut. Bikes like the Trek Madone, with extended seat tubes, or those using seat masts, can complicate comparisons.
Furthermore, mountain bikes often feature kinks or bends in the seat tube. When measuring seat tube length, it’s crucial to measure in a straight line from the bottom bracket center to the top of the seat tube, ignoring any curves in the tube itself.
To measure seat tube length accurately:
- Locate the center of the bottom bracket and the top of the seat tube.
- Use a straight edge to visualize a line connecting these two points, especially if the seat tube is not straight.
- Measure the straight-line distance between the bottom bracket center and the top of the seat tube.
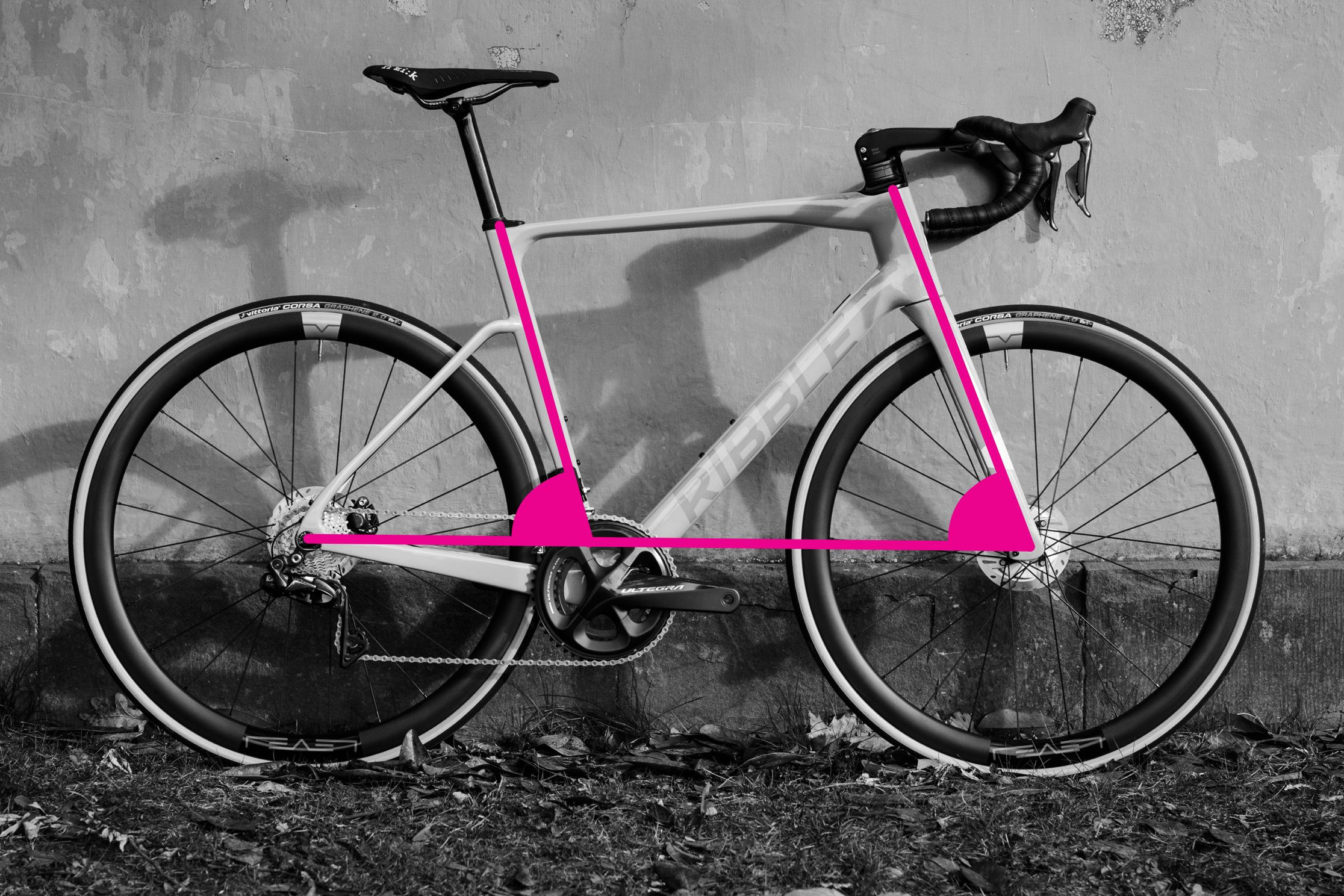
Step-by-Step Guide: Measuring Reach and Stack
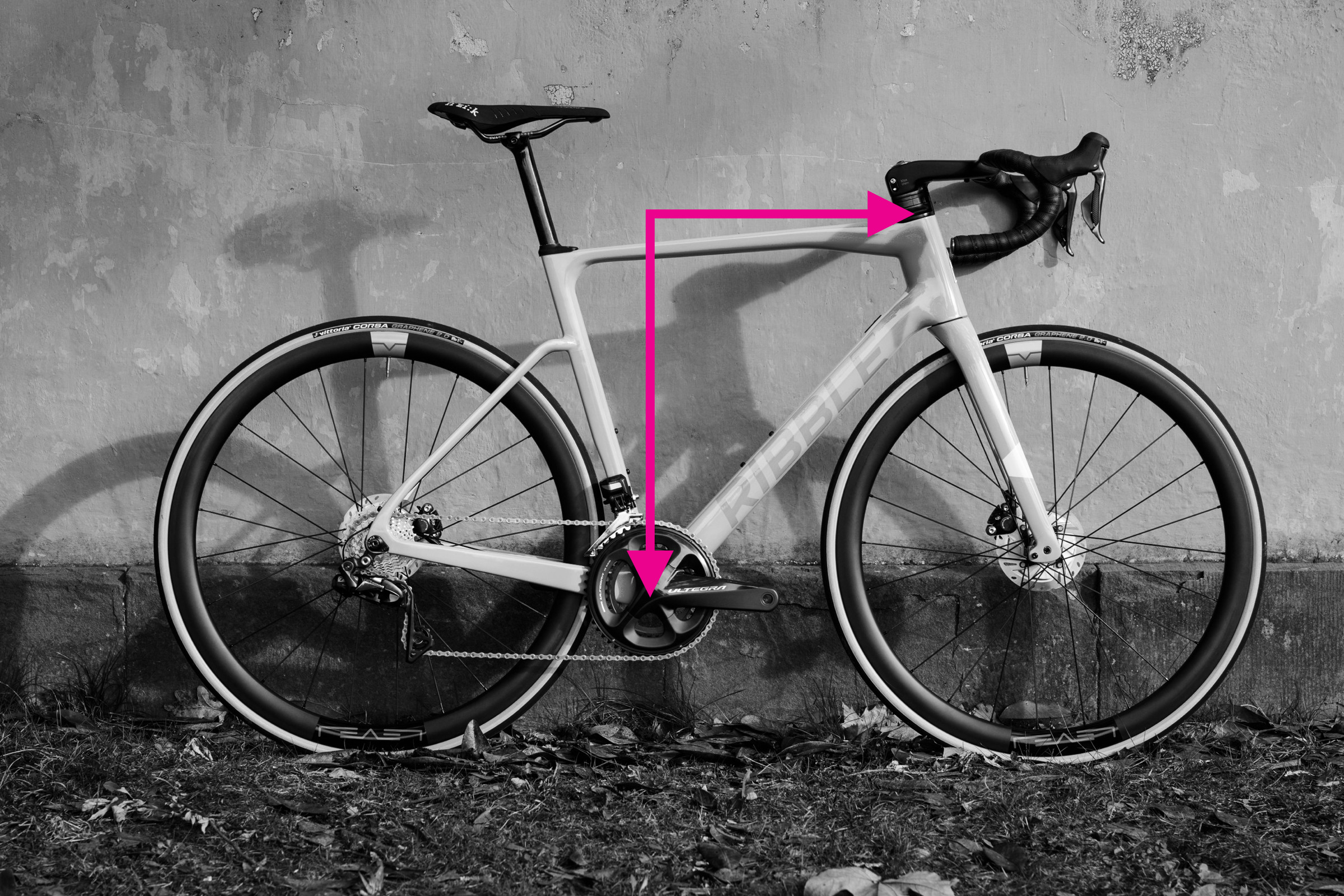 Measuring stack and reach on a bicycle frame
Measuring stack and reach on a bicycle frame
Alt text: Diagram illustrating stack and reach measurements on a bicycle frame, showing horizontal and vertical lines from bottom bracket to head tube.
Reach and stack measurements provide a more consistent way to compare bike frame sizes, as they are independent of traditional frame geometry variations like top tube slope and seat tube extensions. Reach and stack measure the relationship between the bottom bracket and the head tube, two key contact points on the bike.
Reach is the horizontal distance, and stack is the vertical distance between the bottom bracket and the top of the head tube. For a more in-depth explanation of their importance, you can read our article on reach and stack.
Here’s how to measure reach and stack:
Measuring Reach:
- Position your spirit level at the top of the head tube, aligning it with the center.
- Attach a plumb line to the spirit level, ensuring it hangs straight down.
- Adjust the level until the plumb line intersects precisely with the center of the bottom bracket spindle.
- Measure the horizontal distance from the top of the plumb line to the center of the head tube. This is your reach measurement.
Alternatively, you can position your bike against a wall, measure the horizontal distance from the wall to the top of the head tube, and then to the bottom bracket. The difference between these two measurements is the reach.
Measuring Stack:
- Once set up for reach measurement with the plumb line, measure the vertical distance from the spirit level down to the bottom bracket spindle along the plumb line. This is your stack measurement.
Alternatively, measure the vertical distance from the ground to the top of your head tube and then from the ground to the bottom bracket. Subtract the bottom bracket height from the head tube height to get the stack.
Measuring reach and stack can be a bit tricky and may require a second person to assist, especially when using the plumb line method. Repeating the measurements a few times helps ensure accuracy and consistency.
Step-by-Step Guide: Measuring Wheelbase
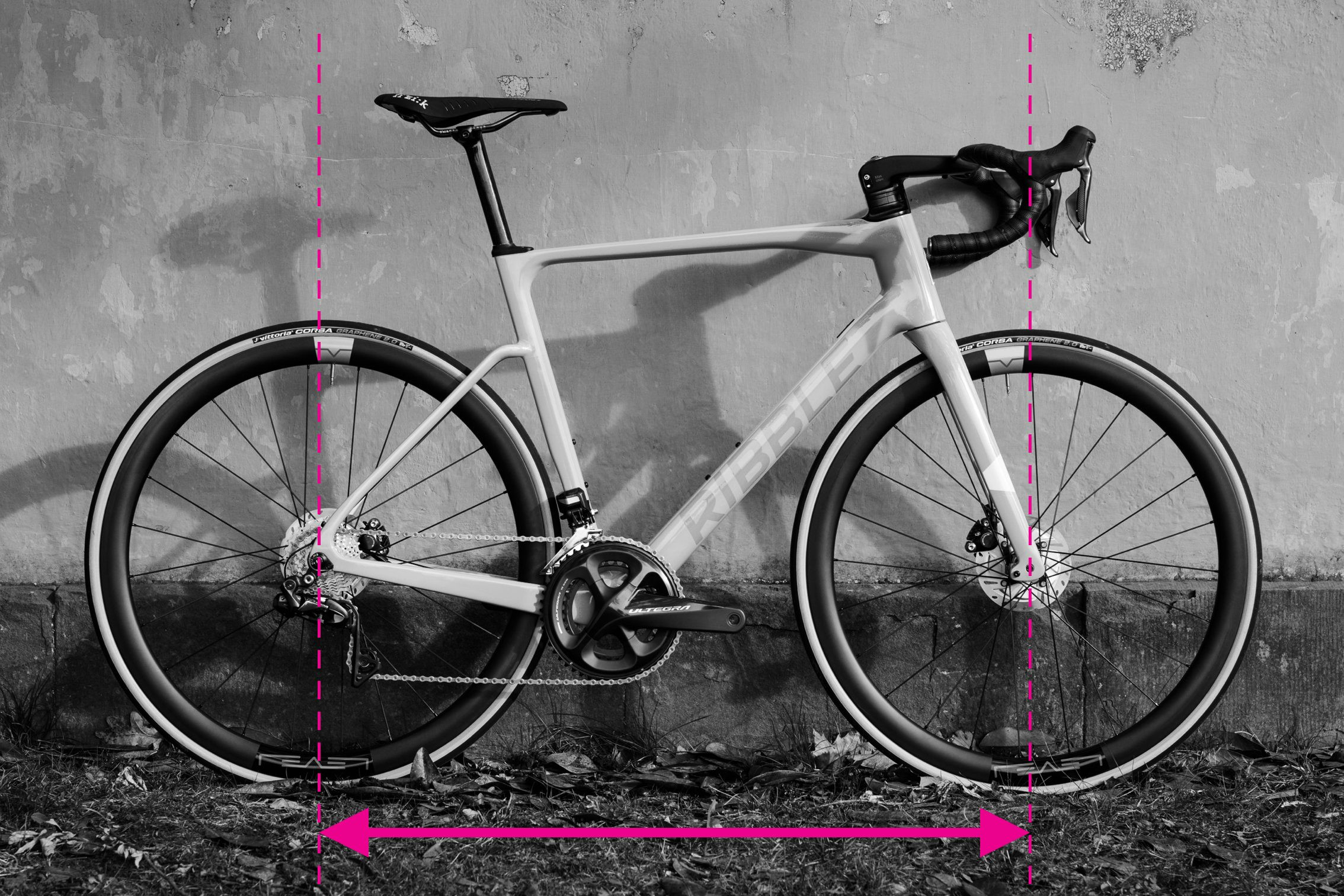 Measuring wheelbase on a bicycle frame
Measuring wheelbase on a bicycle frame
Alt text: Measuring wheelbase on a bicycle, showing tape measure extending from front wheel axle to rear wheel axle.
The wheelbase, the distance between the front and rear axles, significantly influences a bike’s ride quality. It varies with frame size and design, affecting stability and handling.
Measuring wheelbase is relatively simple:
- Ensure your front fork is pointing straight ahead.
- Measure the distance from the center of the front axle to the center of the rear axle.
- For increased accuracy, measure the wheelbase on both sides of the bike and calculate the average to compensate for any slight fork misalignment.
Step-by-Step Guide: Measuring Chainstay Length
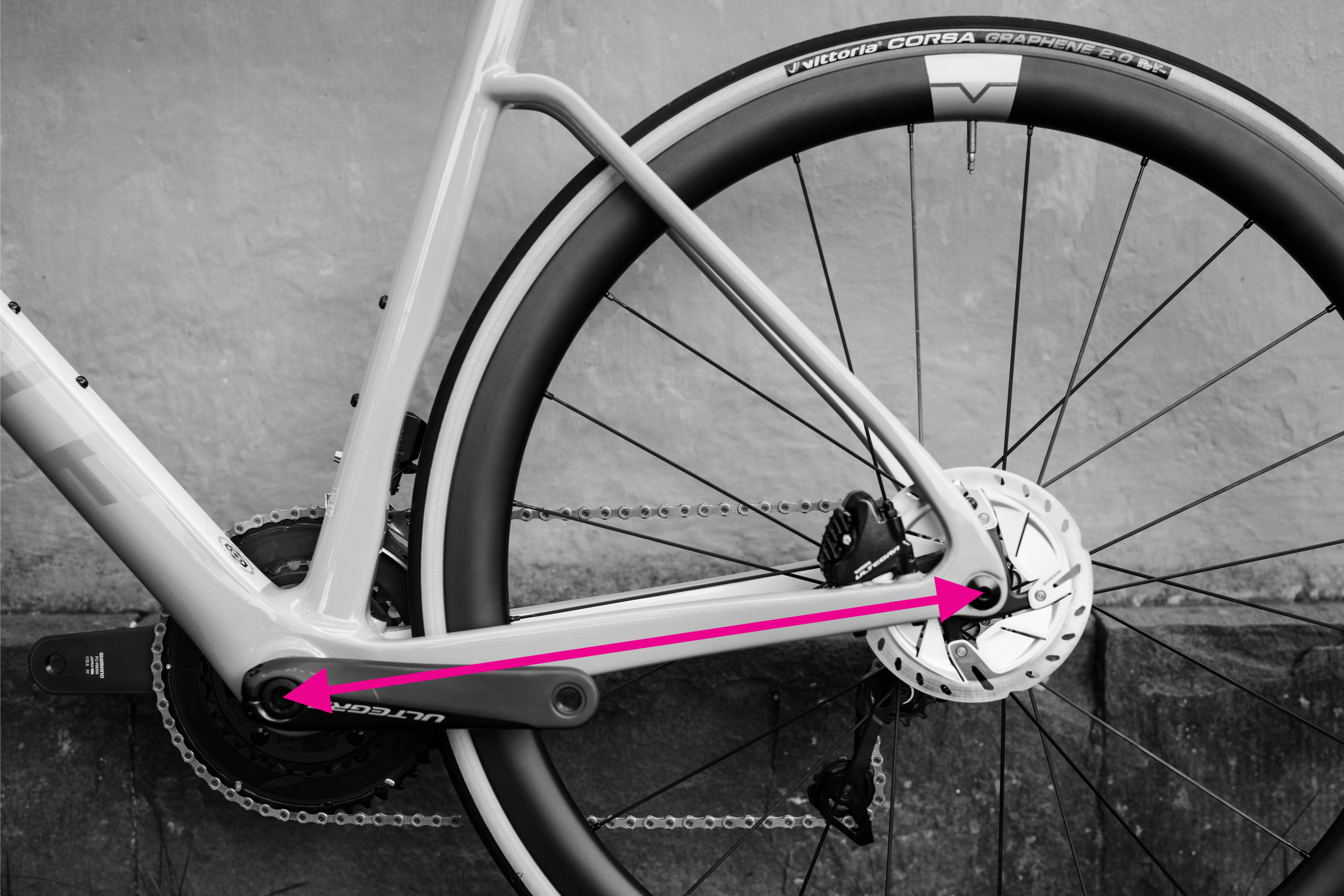 Measuring chainstay length on a bicycle frame
Measuring chainstay length on a bicycle frame
Alt text: Measuring chainstay length on a bike frame with a ruler, from bottom bracket center to rear dropout.
Chainstay length is a component of the wheelbase and plays a crucial role in a bike’s handling characteristics. Shorter chainstays generally result in a more agile and responsive feel, while longer chainstays can offer more stability.
To measure chainstay length:
- Locate the center of the bottom bracket axle and the center of the rear dropout.
- Measure the straight-line distance between these two points. This is your chainstay length.
Step-by-Step Guide: Measuring Front Center
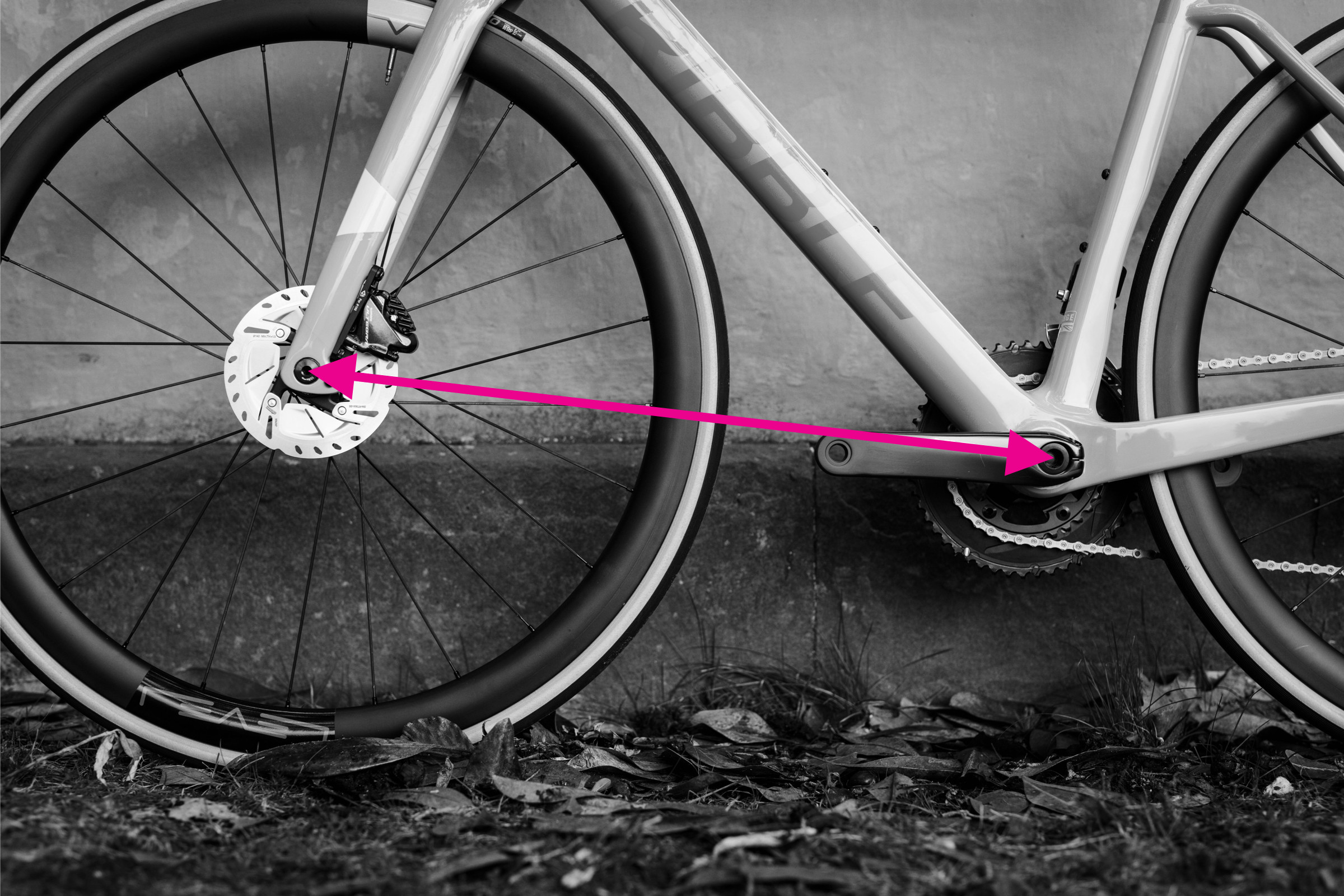 Measuring front center on a bicycle frame
Measuring front center on a bicycle frame
Alt text: Measuring front center on a bicycle frame with a tape measure, from bottom bracket center to front dropout.
Front center is the other component of the wheelbase, analogous to chainstay length but measured to the front dropout. Front center affects handling and, to some extent, toe overlap with the front wheel. While not always listed in standard geometry charts, brands like BMC include it in their specifications.
To measure front center:
- Locate the center of the bottom bracket axle and the center of the front dropout.
- Measure the straight-line distance between these two points. This is your front center.
Note that the wheelbase is not simply the sum of chainstay length and front center because these measurements are not taken along a horizontal plane.
Step-by-Step Guide: Measuring Seat Tube and Head Tube Angles
 Measuring seat tube and head tube angles on a bicycle frame
Measuring seat tube and head tube angles on a bicycle frame
Alt text: Measuring seat tube and head tube angles on a bicycle frame using a clinometer app on a smartphone.
Seat tube angle and head tube angle are critical determinants of a bike’s handling. Steeper angles generally contribute to quicker, more nimble handling. Your clinometer app is essential for measuring these angles.
Measuring Seat Tube Angle:
- If your seat tube is straight, place your smartphone with the clinometer app directly against the seat tube.
- Ensure the bike is vertical and on a level surface for an accurate reading.
- If there’s a kink in the seat tube, use a straight edge to create a straight line from the bottom bracket shell to the top of the seat tube. Then, place your phone against the straight edge to measure the angle.
Measuring Head Tube Angle:
- Newer bikes often have tapered head tubes, making direct measurement slightly complex. To approximate the centerline angle, try to align your phone with the visual center of the head tube or use a straight edge connecting the top and bottom centers of the head tube.
- Alternatively, if your fork legs are straight (without a bend at the crown), you can measure the angle of the fork legs, which will closely correspond to the head tube angle.
- Another method is to measure the angle of the steerer tube extension above the head tube, if accessible.
- Always ensure the bike is vertical when measuring angles.
Step-by-Step Guide: Measuring Bottom Bracket Drop
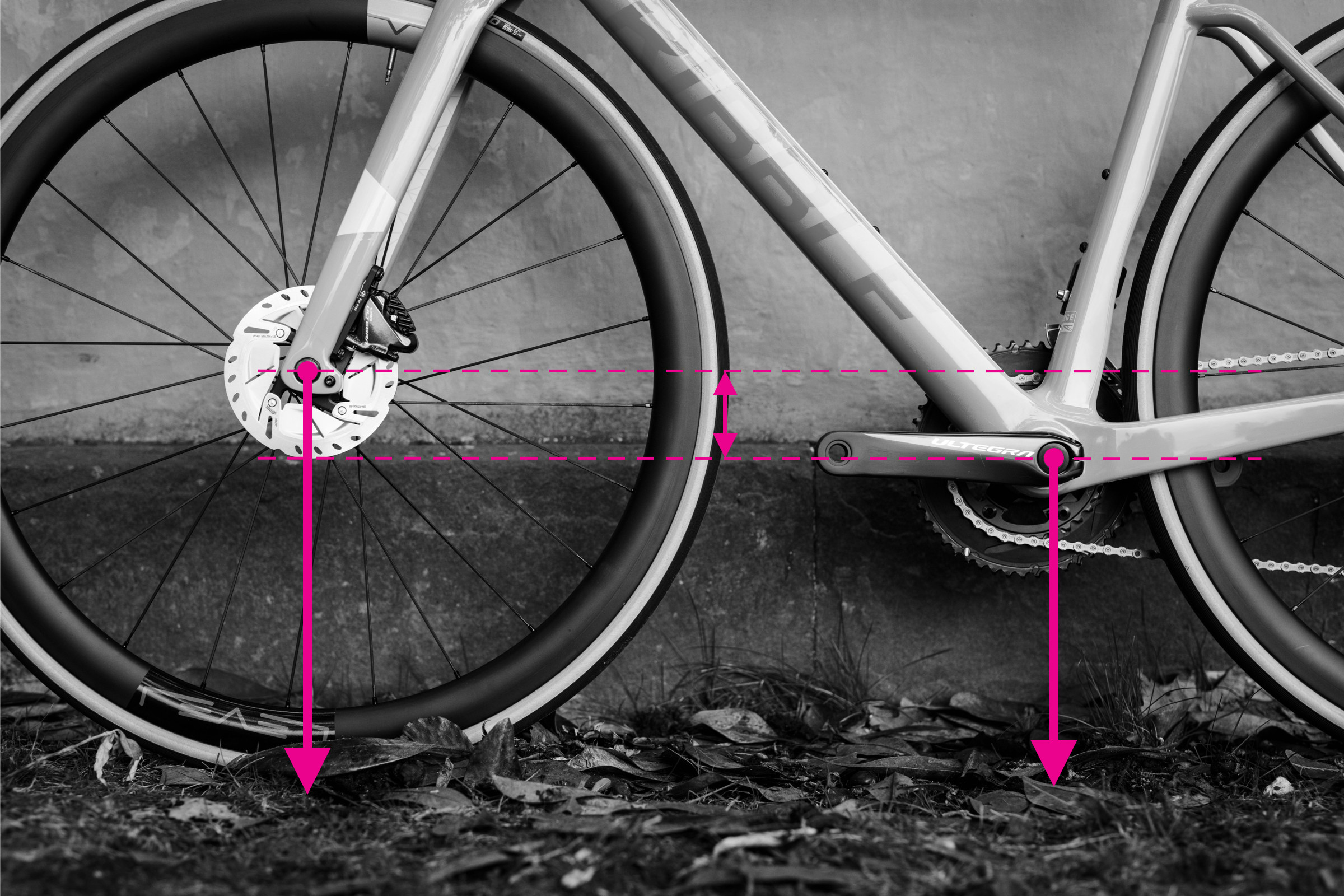 Measuring bottom bracket drop on a bicycle frame
Measuring bottom bracket drop on a bicycle frame
Alt text: Measuring bottom bracket drop on a bicycle frame, showing vertical distance between wheel axle height and bottom bracket height.
Bottom bracket drop is the vertical distance between the wheel axles and the center of the crank axle (bottom bracket). It’s a key measurement that influences stability and cornering.
To measure bottom bracket drop:
- Measure the height from the ground to the rear axle.
- Measure the height from the ground to the center of the bottom bracket.
- Subtract the axle height from the bottom bracket height. The result is your bottom bracket drop.
Step-by-Step Guide: Measuring Bottom Bracket Height
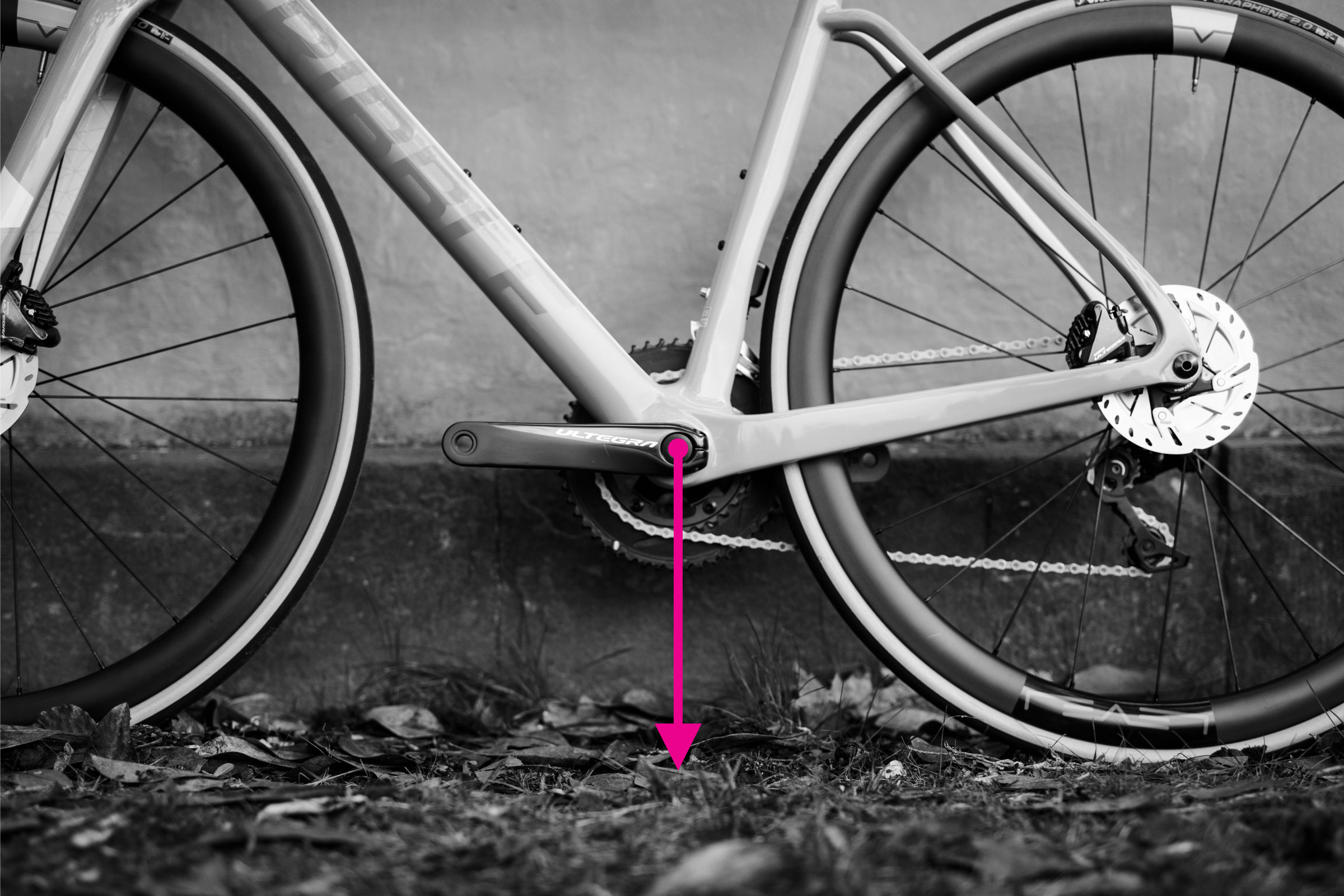 Measuring bottom bracket height on a bicycle frame
Measuring bottom bracket height on a bicycle frame
Alt text: Measuring bottom bracket height on a bicycle frame, showing vertical distance from ground to bottom bracket center.
Bottom bracket height is simply the distance from the ground to the center of the bottom bracket shell. It affects ground clearance and the bike’s center of gravity.
To measure bottom bracket height:
- Ensure your tires are inflated to your standard riding pressure, as tire pressure can slightly affect this measurement.
- Measure the vertical distance from the ground to the center of the bottom bracket shell.
- Keep the bike upright to ensure an accurate measurement.
By taking these measurements, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of your bike frame size and geometry. This knowledge is invaluable when making future bike purchasing decisions, whether you’re looking for a new or second-hand road bike, a commuting bike, or a versatile gravel bike. Keep your measurements in a safe place for easy reference!
