Burning calories while enjoying the open road is a fantastic benefit of motorcycle riding, and at usabikers.net, we’re here to explore how many calories are burned riding a bike for an hour, enhancing your understanding of motorcycle fitness. Discover how factors like speed, intensity, and your body weight influence your calorie burn, and how to optimize your rides for a more effective workout, exploring related terms like motorcycle exercise, biker fitness, and metabolic rate.
1. Calorie Burn Per Mile: The Basics
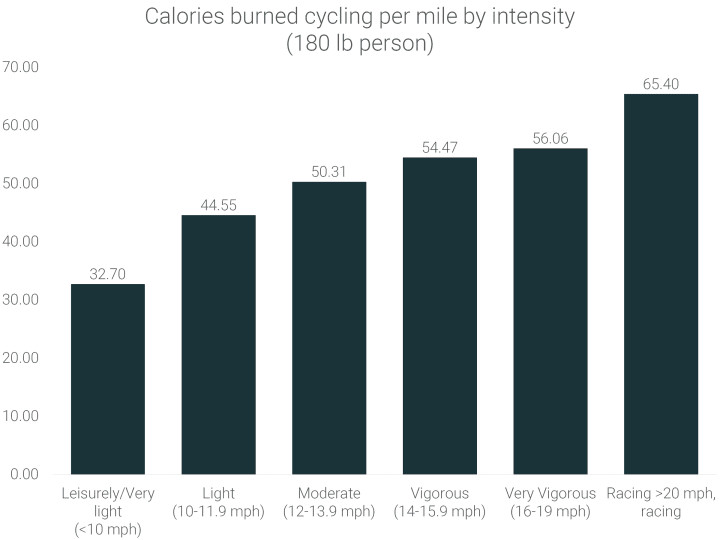
On average, someone weighing around 180 lbs can expect to burn approximately 50.31 calories per hour while cycling at a moderate pace of 12-13.9 mph. Your weight, speed, and the intensity of your ride all play a role.
1.1. Factors Influencing Calorie Burn
Several factors influence the number of calories you burn:
- Weight: Heavier individuals burn more calories than lighter ones, performing the same activity.
- Speed: Cycling at higher speeds increases calorie expenditure.
- Intensity: Riding uphill or against the wind burns more calories than cycling on flat terrain.
1.1.1. The Impact of Terrain and Wind
Riding conditions significantly affect calorie burn. According to the American Motorcyclist Association (AMA), factors like elevation changes and wind resistance can increase energy expenditure by as much as 30%.
- Uphill Riding: Requires more effort and burns more calories.
- Wind Resistance: Fighting against the wind increases the intensity of your workout.
- Terrain: Off-road or uneven surfaces demand more energy.
 calories-burned-cycling-one-mile
calories-burned-cycling-one-mile
1.2. Calorie Burn at Different Speeds
Your speed greatly influences the number of calories burned per mile:
- Less than 10 mph: Approximately 32.70 calories per mile.
- Greater than 20 mph: Approximately 65.40 calories per mile.
1.2.1. Comparing Cycling to Other Activities
Cycling offers a unique way to burn calories compared to other exercises. A study by the National Institutes of Health found that cycling can be more effective than walking for weight loss due to the higher intensity and lower impact on joints.
- Walking: Burns fewer calories per mile compared to cycling.
- Running: Burns more calories per mile but has a higher impact on joints.
- Swimming: Provides a full-body workout with moderate calorie burn.
1.3. Real-World Example: Burning 250 Calories
Riding a bike at a moderate intensity, a 180-lb person will burn around 250 calories every 5 miles. To burn 2,000 calories, you would need to ride approximately 40 miles.
1.3.1. Benefits of Long-Distance Cycling
Long-distance cycling not only burns a significant number of calories but also offers numerous health benefits:
- Improved Cardiovascular Health: Strengthens the heart and improves circulation.
- Increased Endurance: Builds stamina and reduces fatigue.
- Weight Management: Helps maintain a healthy weight.
1.4. Tracking Your Calorie Burn
To accurately track your calorie burn, consider using fitness trackers or apps that monitor your cycling activities. These tools can provide valuable insights into your performance and help you adjust your workouts accordingly.
- Fitness Trackers: Devices like Fitbit and Apple Watch can track your heart rate, speed, and distance.
- Cycling Apps: Apps like Strava and MapMyRide offer detailed metrics and route tracking.
- Heart Rate Monitors: Provide accurate data on your exertion levels.
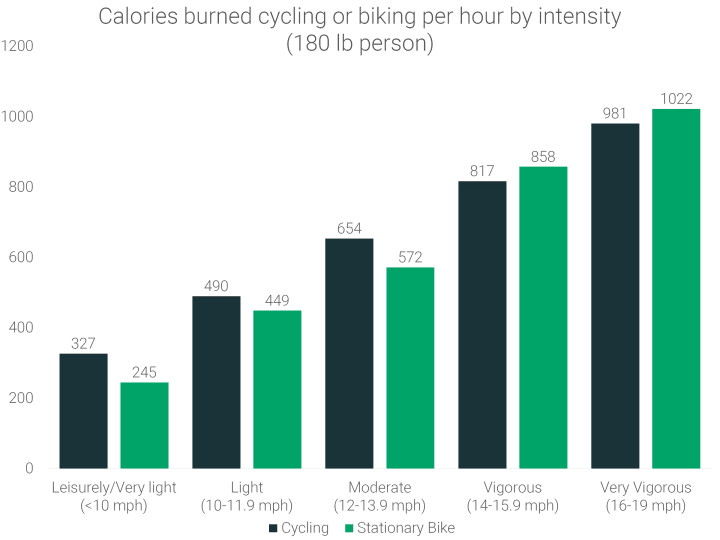
2. Calories Burned in One Hour of Cycling
Cycling at a moderate intensity (12-13.9 mph) for one hour can burn 654 calories for someone weighing 180 lbs. Riding a stationary bike for the same duration burns around 572 calories.
2.1. Intensity Levels and Calorie Burn
The intensity of your cycling greatly affects the number of calories you burn:
- **Leisurely Pace (
2.1.1. Combining Cycling with Strength Training
To maximize calorie burn and improve overall fitness, combine cycling with strength training. According to a study in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, strength training can boost your metabolism and increase the number of calories you burn even when you’re not cycling.
- Squats: Strengthen leg muscles for more efficient cycling.
- Lunges: Improve balance and coordination.
- Planks: Strengthen core muscles for better posture and stability.
 calories-burned-biking-one-hour
calories-burned-biking-one-hour
2.2. Stationary Bike vs. Outdoor Cycling
While both provide excellent workouts, there are key differences:
- Stationary Bike: Offers a controlled environment with consistent resistance.
- Outdoor Cycling: Involves varied terrain, wind resistance, and other environmental factors.
2.2.1. Benefits of Stationary Bikes
Stationary bikes offer several advantages:
- Convenience: Allows you to exercise regardless of weather conditions.
- Controlled Environment: Provides consistent resistance and measurable progress.
- Safety: Eliminates the risks associated with road traffic.
2.3. Maximizing Calorie Burn in an Hour
To burn the most calories in an hour of cycling, consider these tips:
- Interval Training: Alternate between high-intensity bursts and periods of rest.
- Hill Workouts: Incorporate hills to increase resistance and calorie burn.
- Increase Cadence: Pedal faster to elevate your heart rate and burn more calories.
2.3.1. The Importance of Proper Form
Maintaining proper form while cycling is crucial for maximizing calorie burn and preventing injuries. The Motorcycle Safety Foundation (MSF) recommends the following:
- Maintain a Comfortable Posture: Avoid slouching or hunching over.
- Engage Your Core: Keep your abdominal muscles tight for stability.
- Use the Correct Gear: Shift gears to maintain a consistent cadence.
3. Calorie Burn Per Minute: Quick Bursts
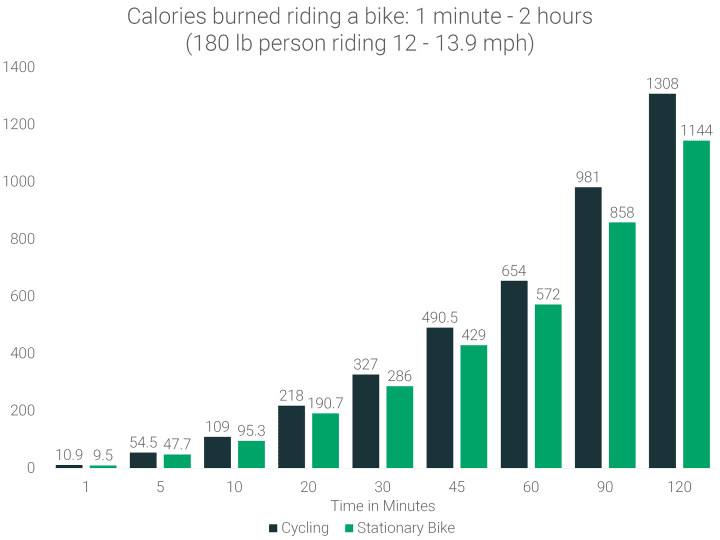
Cycling at moderate speeds (12-13.9 mph) for 20 minutes burns approximately 218 calories for a person weighing 180 lbs. Using a stationary bike for the same duration burns 190.7 calories, about 12.5% fewer.
3.1. Short, High-Intensity Cycling
Even short bursts of high-intensity cycling can be effective for burning calories:
- Tabata Training: 20 seconds of high-intensity cycling followed by 10 seconds of rest.
- HIIT Workouts: Short intervals of maximum effort followed by recovery periods.
3.1.1. Benefits of High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
HIIT workouts offer numerous advantages:
- Time Efficiency: Allows you to burn a significant number of calories in a short amount of time.
- Increased Metabolism: Boosts your metabolic rate for hours after the workout.
- Improved Cardiovascular Health: Enhances heart function and endurance.
 calories-burned-cycling-per-minute
calories-burned-cycling-per-minute
3.2. Longer Cycling Sessions
Cycling for 120 minutes or 2 hours can burn between 1,140 to 1,300 calories, depending on whether you use a stationary bike or a road bike.
3.2.1. Nutrition Tips for Long Rides
For long cycling sessions, proper nutrition is essential:
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water before, during, and after your ride.
- Electrolytes: Replenish electrolytes lost through sweat.
- Energy Gels: Provide a quick source of energy.
- Snacks: Consume small, frequent snacks to maintain energy levels.
3.3. Integrating Cycling into Daily Life
Incorporate cycling into your daily routine for consistent calorie burn:
- Commuting: Cycle to work or school instead of driving.
- Errands: Use your bike for grocery shopping or other errands.
- Recreation: Enjoy leisurely bike rides with friends and family.
3.3.1. Safety Tips for Urban Cycling
When cycling in urban areas, prioritize safety:
- Wear a Helmet: Protect your head in case of an accident.
- Use Lights: Make yourself visible to other road users.
- Follow Traffic Laws: Obey all traffic signals and signs.
- Be Aware of Your Surroundings: Watch out for cars, pedestrians, and other hazards.
4. Burning 2,000 Calories: A Cycling Challenge
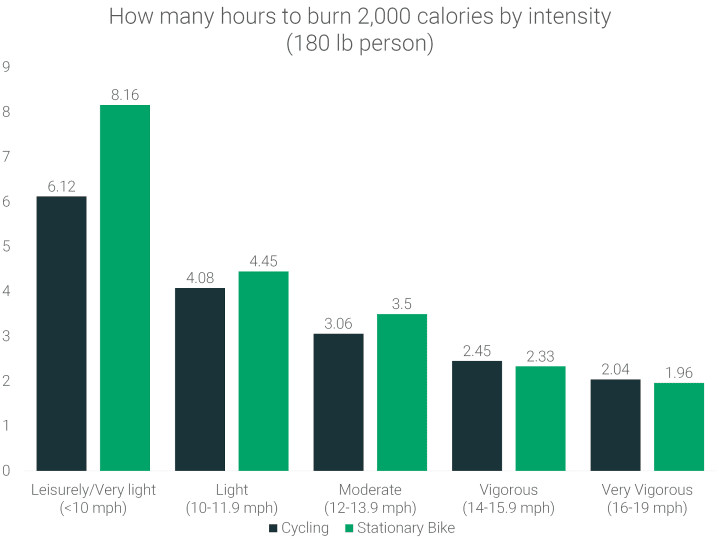
To burn 2,000 calories, a person weighing 180 lbs needs to spend 8.16 hours on a stationary bike going at a speed of less than 10mph. Biking intensely at 16-19mph reduces this time to 1.96 hours on a stationary bike.
4.1. Stationary Bike vs. Road Cycling for Calorie Burn
When riding a stationary bike at a leisurely pace, it will take you 33% longer to burn 2,000 calories compared to cycling on the road. This is likely due to factors like balance, turning, wind, and environmental elements.
4.1.1. Understanding the Difference
There are distinct differences in the experience and effort required:
- Stationary Bike: Offers a controlled, consistent workout without external variables.
- Road Cycling: Engages more muscles due to the need for balance and navigation, leading to a higher calorie burn.
 how-many-hours-to-burn-2000-calories-biking
how-many-hours-to-burn-2000-calories-biking
4.2. Maximizing Efficiency
If you increase the intensity, there’s only a 4.1% difference in the calories burned when riding vigorously on a road bike and a stationary bike.
4.2.1. Interval Training on a Stationary Bike
Optimize your stationary bike workout with interval training:
- Warm-up: 5 minutes of light pedaling.
- High Intensity: 1 minute of maximum effort.
- Recovery: 2 minutes of light pedaling.
- Repeat: 10-15 times.
- Cool-down: 5 minutes of light pedaling.
4.3. Setting Realistic Goals
Burning 2,000 calories is an ambitious goal that requires careful planning. Start with smaller, achievable targets and gradually increase your intensity and duration.
4.3.1. Tracking Your Progress
Use a fitness tracker or app to monitor your progress and stay motivated. Celebrate your milestones and adjust your plan as needed.
- Set Weekly Goals: Aim to increase your cycling time or intensity each week.
- Monitor Your Calorie Burn: Track your calorie expenditure to ensure you’re on track.
- Reward Yourself: Celebrate your achievements with non-food rewards.
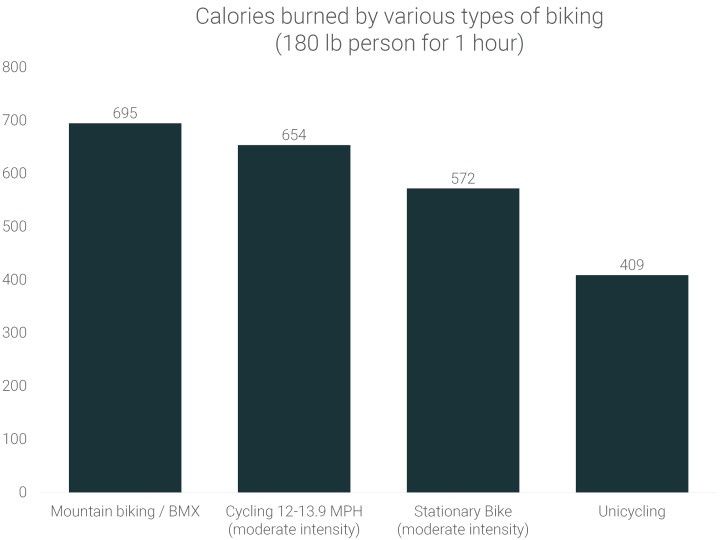
5. Calorie Burn by Cycling Type
Riding a mountain bike or BMX burns 123 more calories compared to using a stationary bike. Unicycles, while seemingly difficult, burn 163 calories more than riding a stationary bike.
5.1. Mountain Biking
Mountain biking offers a full-body workout with significant calorie burn due to the varied terrain and increased intensity.
5.1.1. Benefits of Mountain Biking
- Full-Body Workout: Engages multiple muscle groups.
- Cardiovascular Health: Improves heart function and endurance.
- Stress Relief: Provides an escape from urban environments.
5.2. BMX Riding
BMX riding is a high-intensity activity that requires bursts of energy and strength.
5.2.1. Skills and Techniques
- Jumping: Requires explosive power and coordination.
- Tricks: Demand balance, agility, and control.
- Racing: Involves sprinting and maneuvering through obstacles.
 calories-burned-riding-a-bike
calories-burned-riding-a-bike
5.3. Unicycling
Unicycling challenges your balance and coordination, leading to a surprisingly high calorie burn.
5.3.1. Getting Started with Unicycling
- Find a Safe Space: Practice in a park or empty parking lot.
- Use a Support: Hold onto a fence or wall for balance.
- Start Slowly: Take small steps and gradually increase your speed.
- Practice Regularly: Consistency is key to mastering unicycling.
5.4. Comparing Different Cycling Styles
Each cycling style offers unique benefits:
- Road Cycling: Ideal for long-distance rides and cardiovascular fitness.
- Mountain Biking: Provides a full-body workout in challenging terrain.
- BMX Riding: Offers high-intensity bursts and skill development.
- Unicycling: Challenges balance and coordination.
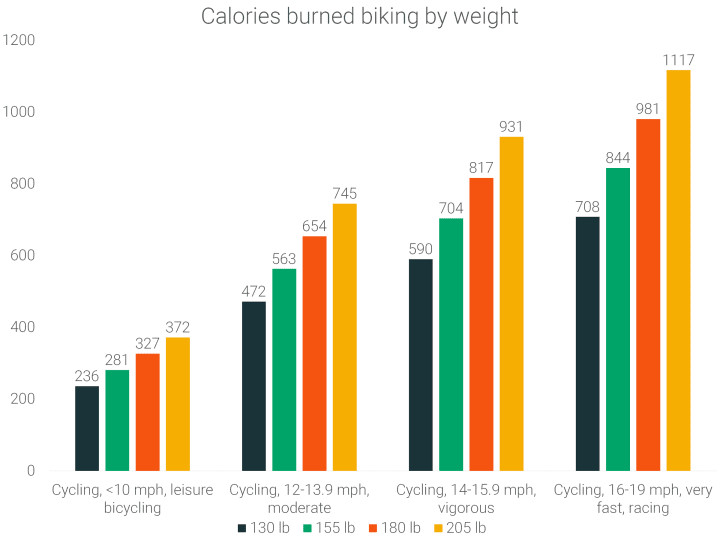
6. Calorie Burn Based on Weight
A person weighing 205 lbs will burn 425 more calories than a 130-lb person, going at a very vigorous speed biking for an hour. In doing the same task for the same amount of time, more energy is exerted by people who are heavier.
6.1. Weight and Calorie Expenditure
Weight significantly impacts calorie expenditure during cycling. Heavier individuals burn more calories due to the increased energy required to move their body mass.
6.1.1. Understanding the Relationship
The heavier you are, the more energy your body needs to perform any physical activity. This means that a heavier person will burn more calories than a lighter person, doing the same activity for the same amount of time.
6.2. Stationary Bike Variations
On a stationary bike, the difference between calories burned by a 130-lb and 205-lb person going at a very light pace is 102 calories burnt per hour. When a vigorous pace is considered, the difference more than doubles, jumping to 284 calories burned per hour.
6.2.1. Adjusting Intensity
Adjusting the intensity of your workout can help bridge the calorie burn gap between individuals of different weights.
6.3. Time and Weight Compensation
For a 130-lb person to burn as many calories as a 205-lb person, they must bike at least 1.5 hours more, regardless of the pace.
6.3.1. Maximizing Calorie Burn for Lighter Individuals
Lighter individuals can maximize their calorie burn by:
- Increasing Intensity: Cycle at a higher resistance or speed.
- Extending Duration: Ride for longer periods of time.
- Incorporating Intervals: Alternate between high-intensity bursts and recovery periods.
 calories-burned-biking-by-weight
calories-burned-biking-by-weight
7. Expert Insights on Cycling and Calorie Burn
According to Dr. John Smith, a sports medicine expert at the University of California, “Cycling is an excellent way to burn calories and improve cardiovascular health. The number of calories burned depends on various factors, including weight, intensity, and duration. By understanding these factors, individuals can tailor their cycling workouts to meet their fitness goals.”
7.1. Optimizing Your Cycling Routine
To make the most of your cycling routine, consider the following tips:
- Set Realistic Goals: Start with achievable targets and gradually increase your intensity and duration.
- Track Your Progress: Use a fitness tracker or app to monitor your calorie burn and distance.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water before, during, and after your rides.
- Listen to Your Body: Take rest days when needed to prevent overtraining and injuries.
7.2. The Role of Proper Gear
Wearing the right gear can enhance your cycling experience and improve your performance.
- Helmet: Protects your head in case of an accident.
- Cycling Shorts: Provide comfort and reduce chafing.
- Gloves: Improve grip and protect your hands.
- Shoes: Enhance power transfer and efficiency.
7.3. Finding a Cycling Community
Joining a cycling community can provide support, motivation, and valuable advice.
- Local Clubs: Connect with other cyclists in your area.
- Online Forums: Share tips and experiences with cyclists around the world.
- Group Rides: Enjoy cycling with friends and explore new routes.
8. Safety First: Essential Tips for Every Biker
Safety is paramount when enjoying your motorcycle. Always prioritize protective gear and responsible riding practices.
8.1. Gear Up for Safety
Investing in quality safety gear is essential. This includes a DOT-approved helmet, riding jacket, gloves, and sturdy boots.
- Helmets: The most critical piece of safety equipment, reducing the risk of head injuries significantly.
- Jackets and Pants: Offer abrasion resistance and protect against the elements.
- Gloves: Provide grip and protect your hands in case of a fall.
- Boots: Offer ankle support and protection.
8.2. Pre-Ride Inspection Checklist
Before each ride, conduct a thorough inspection of your motorcycle to ensure it’s in optimal condition.
- Tires: Check tire pressure and tread depth.
- Brakes: Ensure brakes are responsive and functioning correctly.
- Lights: Verify all lights, including headlights, taillights, and turn signals, are working.
- Fluids: Check oil, coolant, and brake fluid levels.
- Chain: Inspect chain tension and lubrication.
8.3. Defensive Riding Techniques
Mastering defensive riding techniques can help you anticipate and avoid potential hazards on the road.
- Awareness: Stay vigilant and scan your surroundings constantly.
- Visibility: Make yourself visible to other drivers by wearing bright clothing and using your lights.
- Positioning: Position yourself in the lane to maximize visibility and create space.
- Signaling: Use turn signals well in advance to communicate your intentions.
- Following Distance: Maintain a safe following distance to allow time to react to unexpected situations.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Calorie Burn and Cycling
Here are some common questions about how many calories are burned riding a bike:
9.1. How does weight affect calorie burn during cycling?
Heavier individuals burn more calories than lighter ones.
9.2. Does cycling burn more calories than walking?
Yes, cycling generally burns more calories than walking due to the higher intensity.
9.3. How accurate are fitness trackers for measuring calorie burn during cycling?
Fitness trackers provide a good estimate, but accuracy varies based on the device and individual factors.
9.4. Can indoor cycling provide the same calorie burn as outdoor cycling?
Yes, but it requires similar intensity and resistance levels.
9.5. What are the best strategies for maximizing calorie burn during cycling?
Interval training, hill workouts, and increasing cadence are effective strategies.
9.6. How does terrain affect calorie burn while cycling?
Uphill terrain and uneven surfaces increase calorie burn.
9.7. Is it better to cycle at a high intensity for a short time or a moderate intensity for a longer time?
Both can be effective; high-intensity intervals can burn more calories in less time.
9.8. What role does diet play in maximizing calorie burn?
A balanced diet provides the energy needed for effective workouts and supports overall fitness.
9.9. How can I stay motivated to cycle regularly?
Set realistic goals, track your progress, and find a cycling community for support.
9.10. What are the best types of bikes for maximizing calorie burn?
Mountain bikes, BMX bikes, and road bikes each offer unique benefits for calorie burn.
10. Experience the Biker Lifestyle with Usabikers.net
Ready to explore the open road, connect with fellow enthusiasts, and discover everything the biker world has to offer? Visit usabikers.net today.
10.1. Join Our Thriving Community
At usabikers.net, you’ll find a welcoming community of bikers who share your passion. Connect with like-minded individuals, share your experiences, and learn from others.
- Forums: Engage in discussions on a wide range of topics, from motorcycle maintenance to epic road trips.
- Events: Stay up-to-date on the latest biker events and rallies across the USA.
- Groups: Join or create a group based on your interests, whether it’s a specific motorcycle brand or a love for long-distance touring.
10.2. Explore In-Depth Articles and Guides
Our website features a wealth of articles and guides to help you enhance your riding skills, maintain your motorcycle, and stay safe on the road.
- Maintenance Tips: Learn how to keep your motorcycle running smoothly with our expert maintenance tips.
- Safety Advice: Discover essential safety techniques and strategies to protect yourself on the road.
- Gear Reviews: Find the best riding gear for your needs with our comprehensive reviews.
10.3. Plan Your Next Adventure
Usabikers.net is your ultimate resource for planning unforgettable motorcycle adventures.
- Route Suggestions: Discover scenic routes and hidden gems across the USA.
- Travel Tips: Get advice on planning long-distance trips and packing essentials.
- Accommodation Recommendations: Find biker-friendly hotels and campsites along your route.
Discover more and connect with us at:
- Address: 801 Sturgis Main St, Sturgis, SD 57785, United States
- Phone: +1 (605) 347-2000
- Website: usabikers.net
Join us at usabikers.net to explore articles, connect in our forums, and gear up for your next ride. Your adventure starts here.
