Cycling is a fantastic way to stay active, explore the outdoors, and improve your fitness. Whether you’re cruising down scenic paths or pushing your limits in an intense workout, understanding how many calories you burn riding a bike can be a key motivator and help you achieve your fitness goals. This guide dives deep into the factors influencing calorie burn during cycling, offering data-backed insights to help you optimize your rides for calorie expenditure.
Calories Burned Cycling Per Mile: Factors and Averages
When considering calories burned per mile cycling, several variables come into play. Your weight, the intensity of your ride, and even the terrain can significantly impact the final number.
For an average 180-lb adult cycling at a moderate speed (12-13.9 mph), approximately 50.31 calories are burned per hour. However, breaking this down per mile reveals a more nuanced picture. At moderate speeds, this same individual burns roughly 32.70 to 65.40 calories per mile, with the variance depending on subtle changes in speed and effort.
 calories-burned-cycling-one-mile
calories-burned-cycling-one-mile
To put this into perspective, a 5-mile bike ride at a moderate intensity will help a 180-lb person burn around 250 calories. If your goal is to burn a significant 2,000 calories, you would need to cycle approximately 40 miles at this pace.
Hourly Calorie Burn: Outdoor vs. Stationary Biking
Looking at calories burned cycling per hour provides another useful metric for gauging your workout. An hour of moderate-intensity cycling outdoors (12-13.9 mph) burns around 654 calories for a 180-lb individual. Interestingly, the same person on a stationary bike for an hour at a similar perceived effort might burn slightly fewer calories, around 572. This difference highlights the subtle increase in effort required for outdoor cycling due to factors like wind resistance and terrain variations.
The intensity of your cycling workout dramatically affects calorie expenditure. A leisurely bike ride will burn significantly fewer calories compared to a vigorous session. For example, at a leisurely pace, you might burn as little as 245 calories per hour.
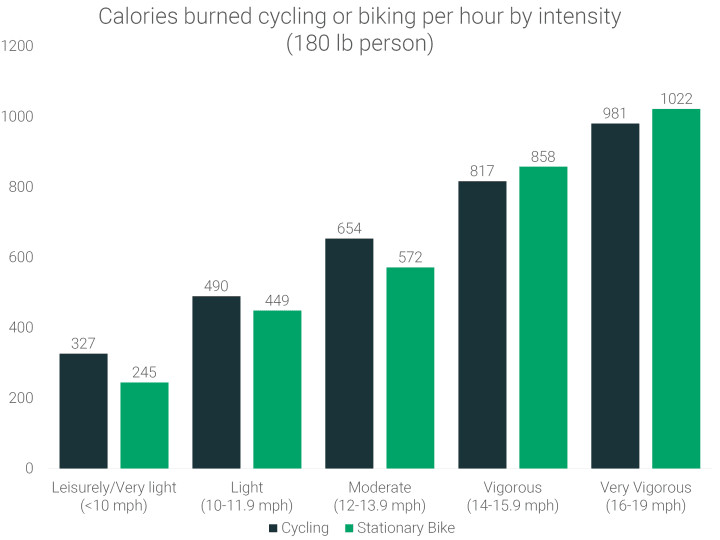 calories-burned-biking-one-hour
calories-burned-biking-one-hour
The data reveals a striking contrast: cycling at a very vigorous pace can burn up to 3 times as many calories as a leisurely ride. Stationary biking shows an even more pronounced difference, with a very vigorous pace burning about 4.17 times more calories than a leisurely one. This underscores the importance of intensity when cycling for calorie burning.
Calorie Burn in Minutes: Short Bursts of Cycling
Even short cycling sessions can contribute to your daily calorie burn. Cycling at a moderate pace (12-13.9 mph) for just 20 minutes can burn approximately 218 calories for a 180-lb person. Stationary biking for the same duration burns slightly less, around 190.7 calories, representing about a 12.5% reduction.
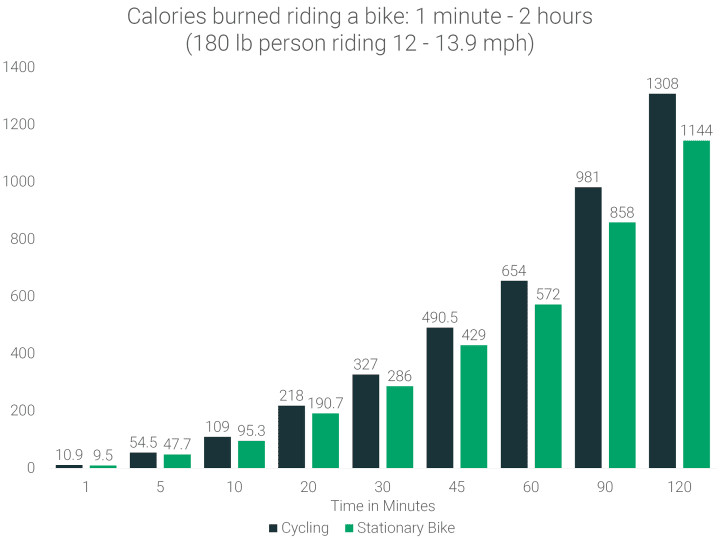 calories-burned-cycling-per-minute
calories-burned-cycling-per-minute
For longer workouts, cycling for 120 minutes, or 2 hours, can result in a substantial calorie burn. Depending on whether you choose a stationary bike or outdoor cycling, you could burn between 1,140 to 1,300 calories respectively in a two-hour session.
Cycling Duration to Burn 2,000 Calories: Time and Intensity Matter
If you have a specific calorie goal in mind, like burning 2,000 calories through cycling, the time required will depend heavily on your intensity. To burn 2,000 calories on a stationary bike at a leisurely pace (less than 10 mph), a 180-lb person would need to cycle for a considerable 8.16 hours. However, ramping up the intensity to a vigorous pace (16-19 mph) drastically reduces the time needed to just 1.96 hours on a stationary bike.
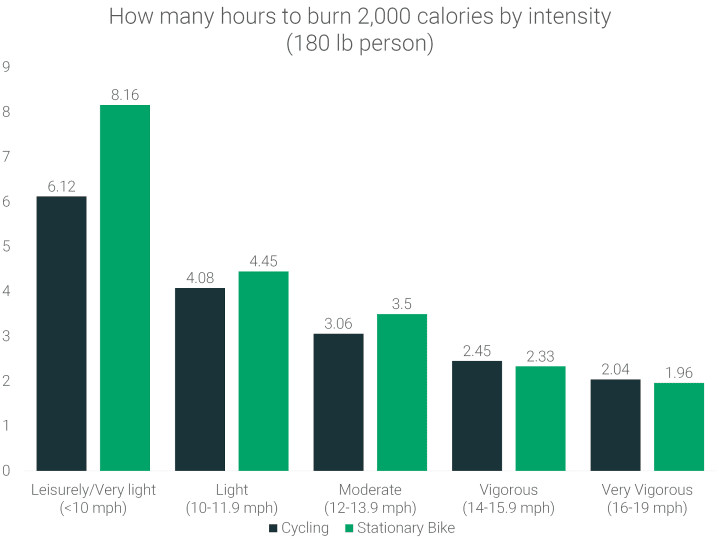 how-many-hours-to-burn-2000-calories-biking
how-many-hours-to-burn-2000-calories-biking
Leisurely stationary biking takes approximately 33% longer to burn the same calories compared to road cycling, likely due to the added engagement of balance, maneuvering, and external factors in outdoor riding. However, when intensity increases, the calorie burn difference between road and stationary biking narrows significantly, with only about a 4.1% difference at vigorous levels.
Calorie Burn Across Different Cycling Types: Choose Your Ride
The type of bike and cycling you choose also influences calorie expenditure. Mountain biking or BMX riding burns approximately 123 more calories per hour compared to stationary biking, reflecting the increased physical demands of navigating varied terrains and bike handling. Interestingly, while unicycling might seem incredibly challenging, it burns fewer calories than mountain biking but still burns about 163 calories more than stationary biking per hour.
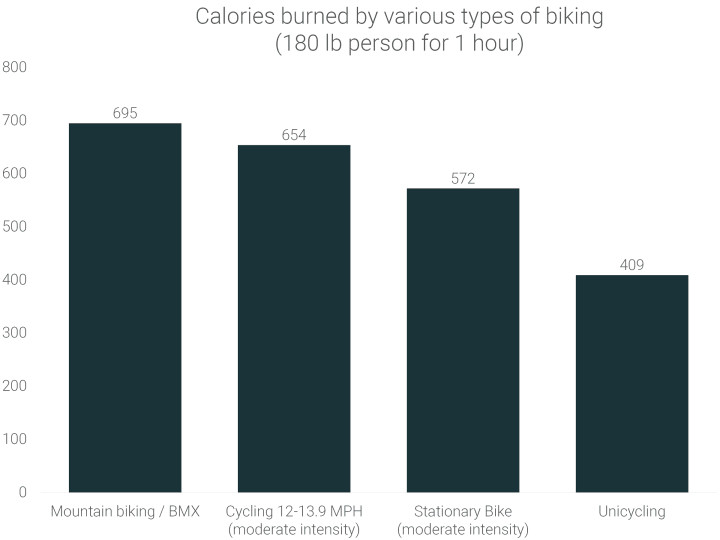 calories-burned-riding-a-bike
calories-burned-riding-a-bike
Weight and Calorie Burn: The Heavier You Are, The More You Burn
Body weight is a significant determinant of calorie burn during any physical activity, including cycling. A person weighing 205 lbs will burn considerably more calories than someone weighing 130 lbs performing the same cycling workout. For example, a 205-lb person can burn 425 more calories per hour than a 130-lb person when cycling at a very vigorous pace. This difference is due to the greater energy expenditure required to move a heavier body mass.
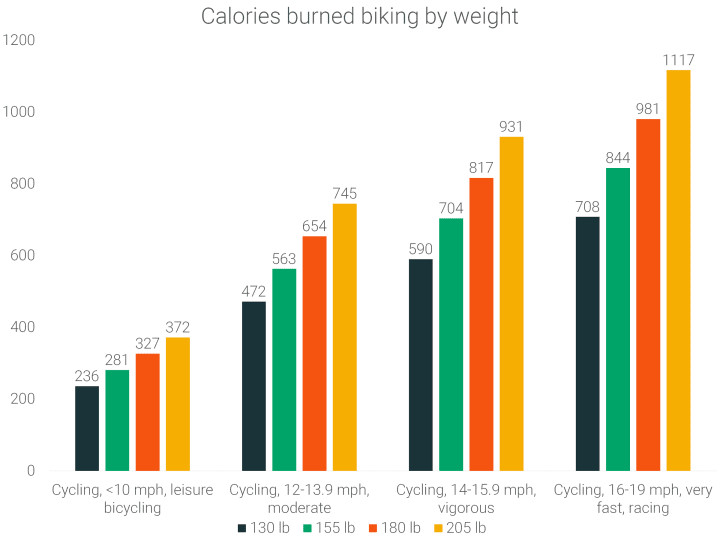 calories-burned-biking-by-weight
calories-burned-biking-by-weight
Even at a very light pace on a stationary bike, the difference in calorie burn between a 130-lb and 205-lb person is around 102 calories per hour. As intensity increases, this gap widens. At a vigorous pace, the calorie burn difference more than doubles to 284 calories per hour. To burn the same number of calories as a heavier person, a lighter individual would need to cycle for approximately 1.5 hours longer, regardless of the intensity level.
Understanding how many calories you burn riding a bike empowers you to tailor your cycling workouts to meet your specific fitness and weight management goals. By considering factors like intensity, duration, bike type, and your own body weight, you can effectively use cycling as a powerful tool for calorie burning and overall health improvement.
