Choosing the right bike frame size is crucial for comfort, efficiency, and overall riding enjoyment. Whether you’re buying a new bicycle, considering a used one, or even renting for a cycling trip, understanding How To Measure A Bike Frame is essential. This guide will walk you through the key measurements, ensuring you select a bike that fits you perfectly and suits your riding style.
Understanding bike frame geometry is not just for seasoned cyclists; it’s vital for beginners too. Manufacturers don’t always use consistent sizing methods, making it important to understand the fundamental measurements yourself. By learning how to accurately measure a bike frame, you can confidently compare different brands and models, ensuring you get the right fit regardless of sizing labels.
This article provides a detailed, step-by-step approach to measuring your bike frame. We will cover all the critical dimensions, from top tube length and seat tube length to reach, stack, and angles. By the end of this guide, you’ll have the knowledge and tools to measure any bike frame and make informed decisions about your next cycling purchase or rental.
Essential Bike Frame Measurements Explained
Before we dive into the “how-to,” let’s define the key bike geometry measurements you’ll be working with. These dimensions dictate how a bike feels and performs on the road or trail.
- Top Tube Length (Effective): The horizontal distance from the center of the head tube to the center of the seat post. This measurement is crucial for reach and rider positioning.
- Seat Tube Length: The distance from the center of the bottom bracket to the top of the seat tube. While less critical for sizing than it once was, it still provides a general frame size indication.
- Reach: The horizontal distance from the bottom bracket to the top center of the head tube. Reach is a primary factor in determining the bike’s cockpit length and rider’s forward lean.
- Stack: The vertical distance from the bottom bracket to the top center of the head tube. Stack height influences handlebar height and rider’s uprightness.
- Wheelbase: The distance between the front and rear wheel axles. Wheelbase affects stability and handling.
- Chainstay Length: The distance between the bottom bracket and the rear axle. Chainstay length impacts the bike’s responsiveness and climbing ability.
- Front Center: The distance from the bottom bracket to the front axle. Front center influences handling and weight distribution.
- Seat Tube Angle: The angle of the seat tube relative to the ground. Seat tube angle affects pedaling efficiency and weight distribution.
- Head Tube Angle: The angle of the head tube relative to the ground. Head tube angle influences steering responsiveness and stability.
- Bottom Bracket Drop: The vertical distance the bottom bracket is below the wheel axles. Bottom bracket drop affects stability and cornering.
- Bottom Bracket Height: The distance from the ground to the center of the bottom bracket. Bottom bracket height affects ground clearance and stability.
Tools You’ll Need for Measuring a Bike Frame
To accurately measure a bike frame, you’ll need a few simple tools. Gathering these beforehand will make the process smooth and efficient.
- Tape Measure: A standard tape measure, preferably metric for consistency, is essential for measuring distances.
- Clinometer (or Smartphone App): A clinometer measures angles. Many free smartphone apps are available that serve this purpose effectively.
- Spirit Level (or Straight Edge with Clinometer App): A long spirit level ensures horizontal and vertical measurements. Alternatively, a straight piece of wood combined with a clinometer app works just as well.
- Plumb Line (or String and Weight): A plumb line creates a vertical reference. You can easily improvise one with string and a small weight like a nut or washer.
While metric units are standard in bike geometry, some manufacturers, particularly for mountain bikes, might still use inches. For consistency and ease of comparison, we recommend using metric units (centimeters and millimeters) throughout the measuring process. If needed, conversion to inches can be done later.
It’s also highly beneficial to check the manufacturer’s website for geometry charts specific to your bike model and year. These charts provide factory measurements and can be a valuable reference point, often more accurate than manual measurements.
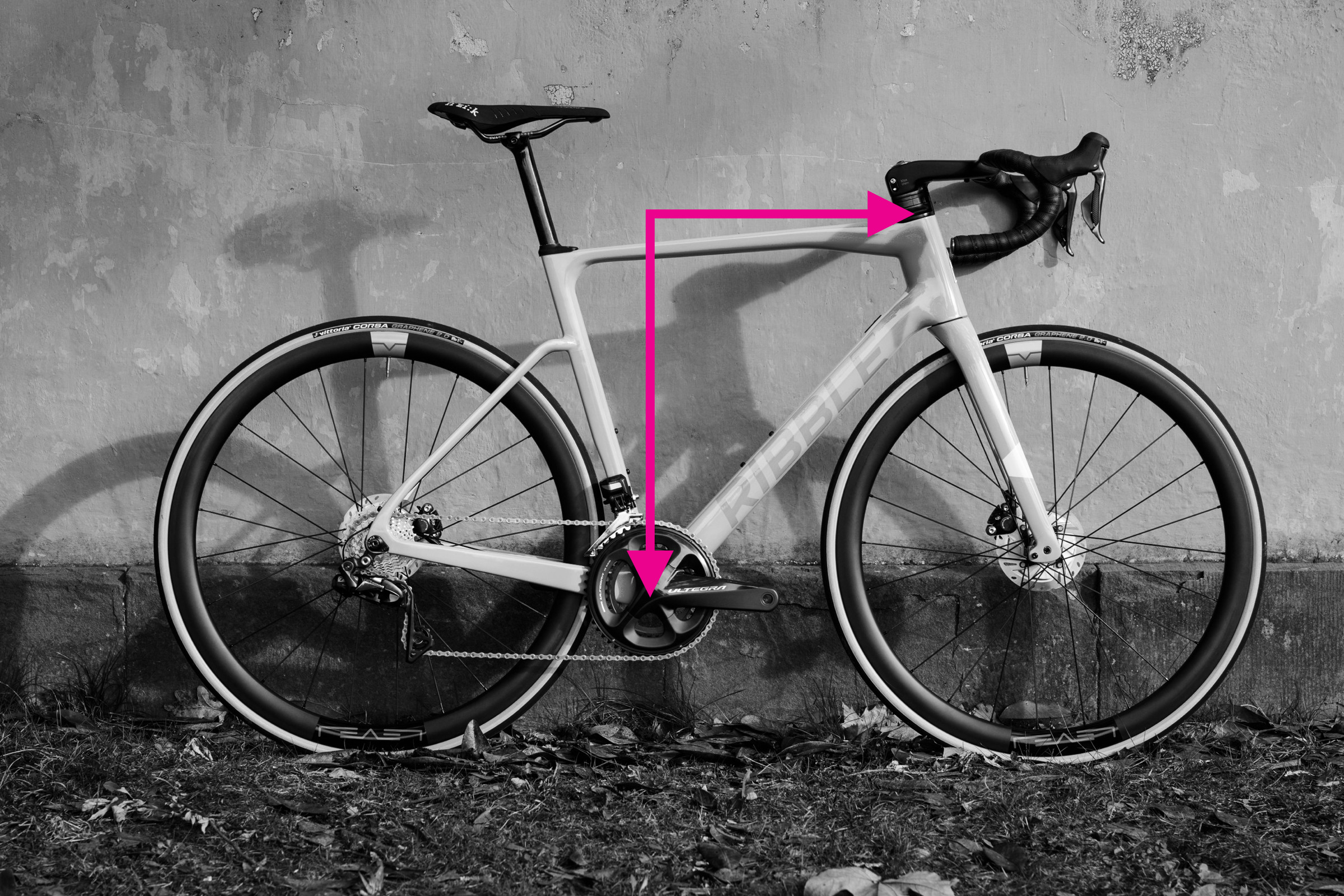
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Measure Top Tube Length
 Measuring top tube length on a bicycle frame
Measuring top tube length on a bicycle frame
The top tube length, specifically the effective or virtual top tube length, is a critical measurement. It represents the horizontal distance between the head tube and seat post centerlines and is a key factor in bike fit. Modern bike designs often feature sloping top tubes, making the effective top tube length more relevant than the actual tube length.
Steps to Measure Top Tube Length:
- Identify Center Points: Locate the center of your head tube and the center of your seat post at the top tube level.
- Horizontal Alignment: Use your spirit level or clinometer app to ensure a perfectly horizontal line from the head tube to the seat post.
- Measure Horizontally: Measure the horizontal distance between the two center points. This is your effective top tube length.
Manufacturers sometimes size road bikes based on top tube length, although mountain bikes and some modern road bikes often use S, M, L sizing. However, sizing conventions vary significantly between brands. A size Medium from one brand might have a different top tube length than a Medium from another. Furthermore, brands may measure virtual top tube length slightly differently, so understanding this measurement method is key for accurate comparisons.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Measure Seat Tube Length
 Measuring seat tube length on a bicycle frame
Measuring seat tube length on a bicycle frame
Seat tube length is measured as a straight line from the center of the bottom bracket to the top of the seat tube. While traditionally used for sizing, it’s less critical now due to varying frame designs and sloping top tubes.
Steps to Measure Seat Tube Length:
- Locate Bottom Bracket Center: Identify the center of the bottom bracket.
- Locate Seat Tube Top: Find the top of the seat tube.
- Straight Line Measurement: Measure the straight-line distance between these two points.
Complications can arise with bikes featuring seat tube extensions above the top tube junction or integrated seatmasts. Mountain bikes often have kinks or bends in the seat tube, so ensure you’re measuring a straight line and not following the tube’s curve. Using a straight edge to align from the bottom bracket center to the seat tube top helps ensure an accurate measurement.
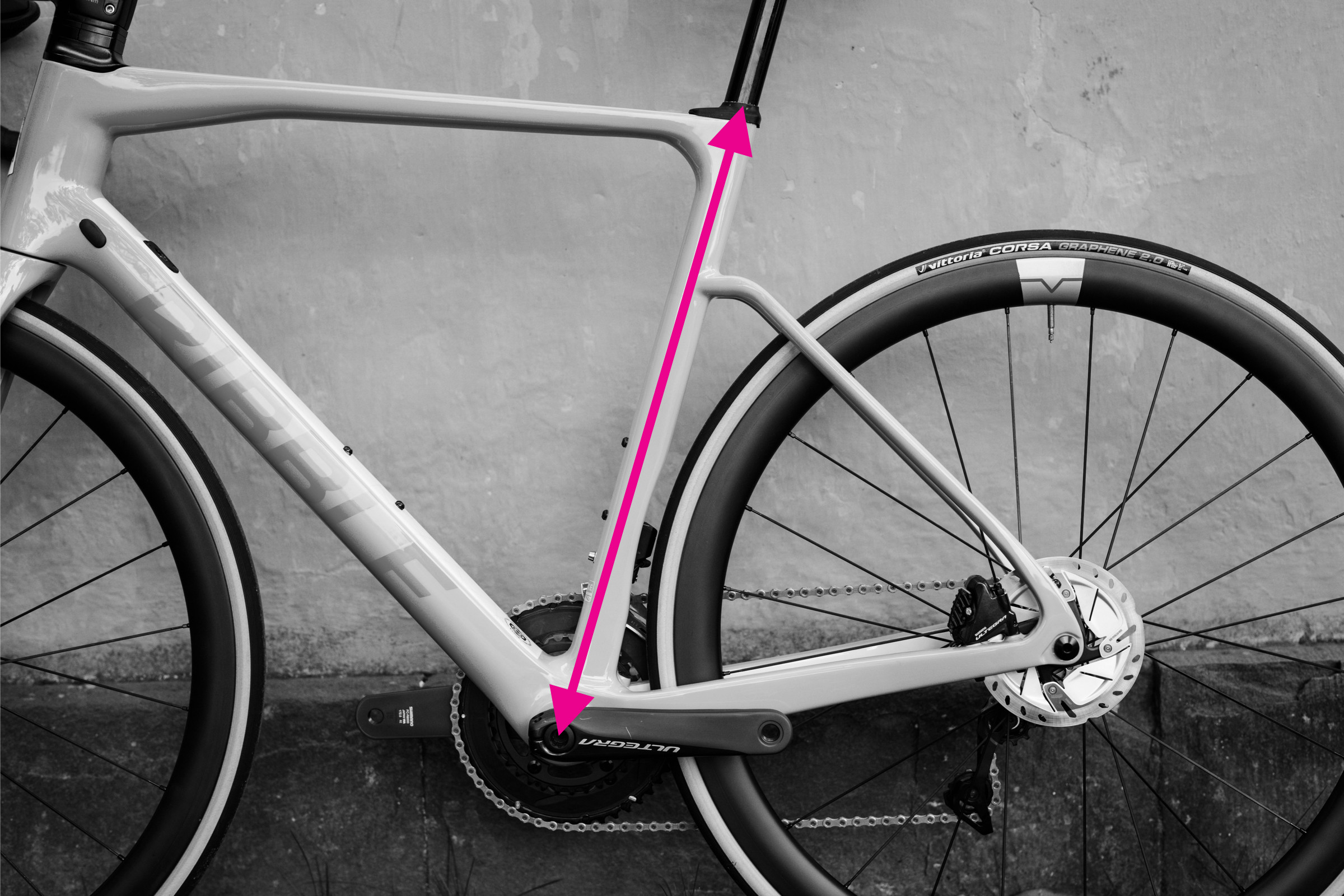
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Measure Reach and Stack
 Measuring stack and reach on a bicycle frame
Measuring stack and reach on a bicycle frame
Reach and stack provide a more consistent and design-independent way to compare bike frame sizes. They measure the horizontal and vertical distances between the bottom bracket and the top of the head tube, two crucial contact points.
Steps to Measure Reach and Stack:
Reach Measurement:
- Level Alignment: Place your spirit level across the top of the head tube, ensuring it extends forward.
- Plumb Line Setup: Attach a plumb line to the edge of the spirit level.
- Bottom Bracket Intersection: Adjust the level until the plumb line hangs directly over the center of the bottom bracket spindle.
- Measure Reach: Measure the horizontal distance from the top of the head tube to the plumb line. This is your reach.
Stack Measurement:
- Vertical Distance: Using the same setup as for reach, measure the vertical distance from the top of the head tube down to the plumb line level with the bottom bracket. This is your stack.
Alternatively, you can measure stack by measuring the vertical distance from the ground to the top of the head tube and then subtracting the height of the bottom bracket from the ground. Both reach and stack can be tricky to measure precisely, so repeating the process and having a second person assist can improve accuracy.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Measure Wheelbase
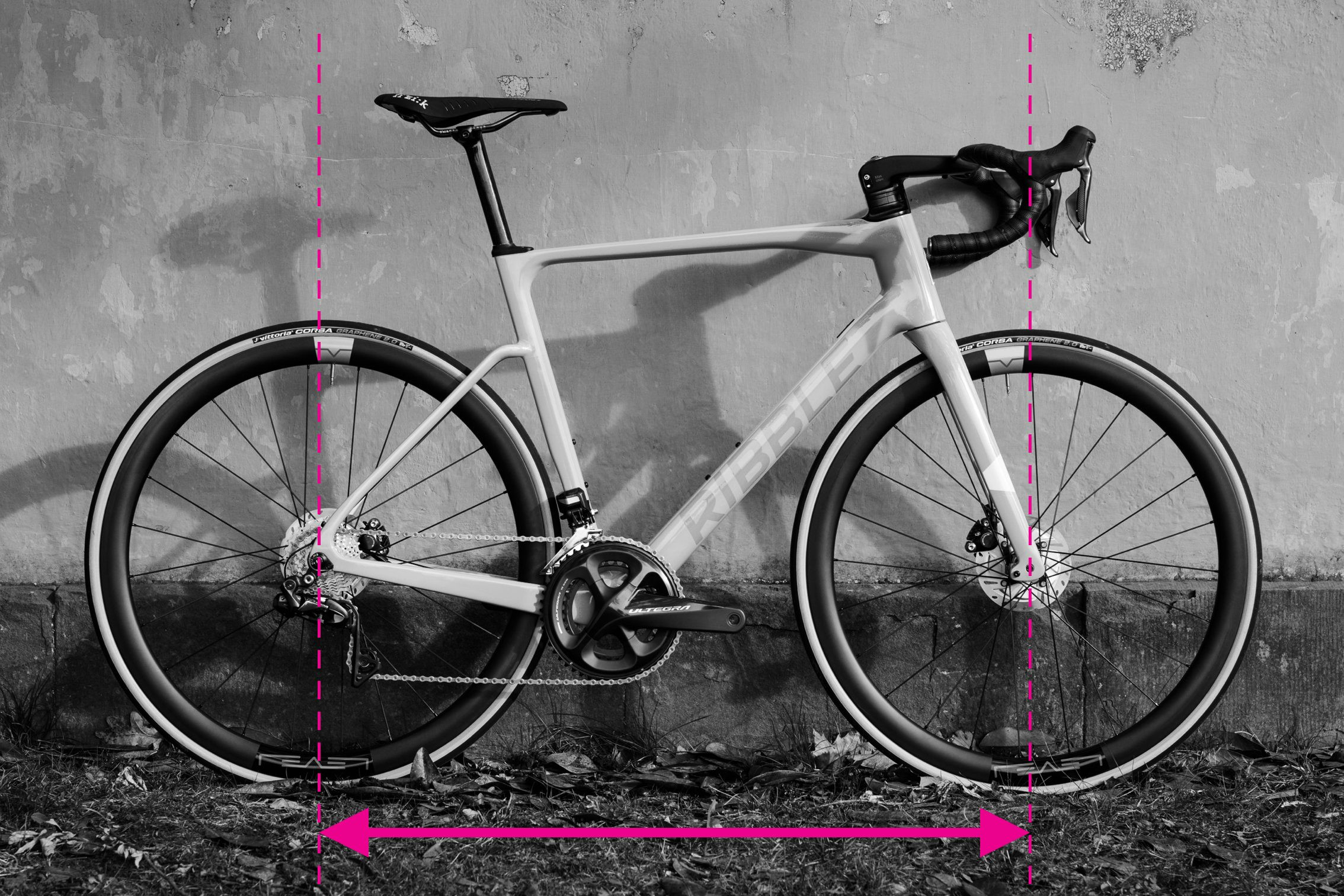 Measuring wheelbase on a bicycle frame
Measuring wheelbase on a bicycle frame
Wheelbase, the distance between the front and rear axles, significantly influences a bike’s ride quality and varies with frame size.
Steps to Measure Wheelbase:
- Straight Fork Alignment: Ensure the front fork is pointing straight ahead.
- Axle to Axle Measurement: Measure the distance from the center of the front axle to the center of the rear axle.
For increased accuracy, especially if the fork alignment is uncertain, measure the wheelbase on both sides of the bike and average the two measurements. This helps compensate for any slight fork misalignment.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Measure Chainstay Length
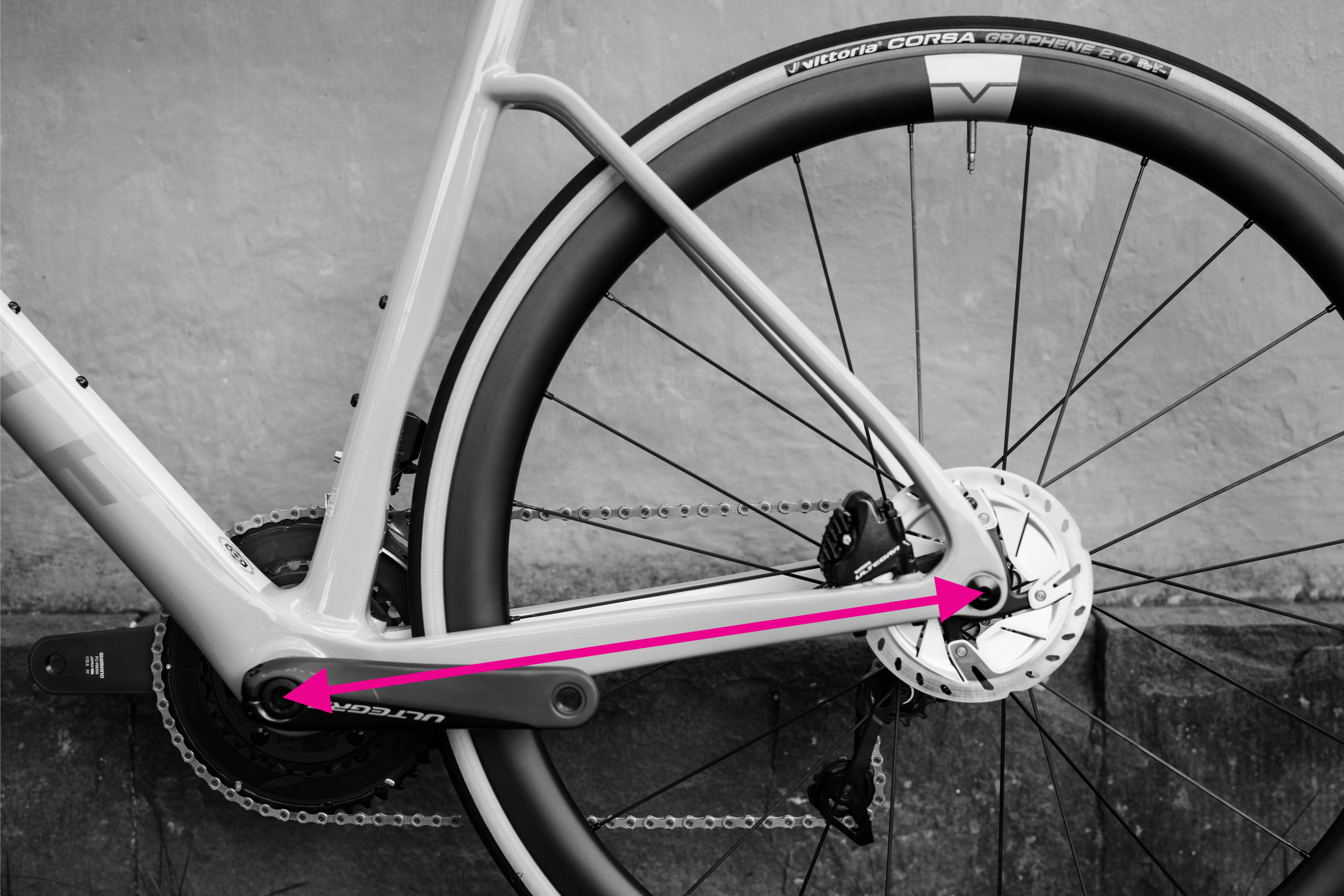 Measuring chainstay length on a bicycle frame
Measuring chainstay length on a bicycle frame
Chainstay length, a component of wheelbase, plays a crucial role in a bike’s handling characteristics. Shorter chainstays generally result in a more agile and responsive feel.
Steps to Measure Chainstay Length:
- Bottom Bracket Center: Locate the center of the bottom bracket.
- Rear Dropout Center: Identify the center of the rear axle dropout.
- Straight Line Distance: Measure the straight-line distance between these two points.
This measurement is relatively straightforward using a tape measure or ruler.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Measure Front Center
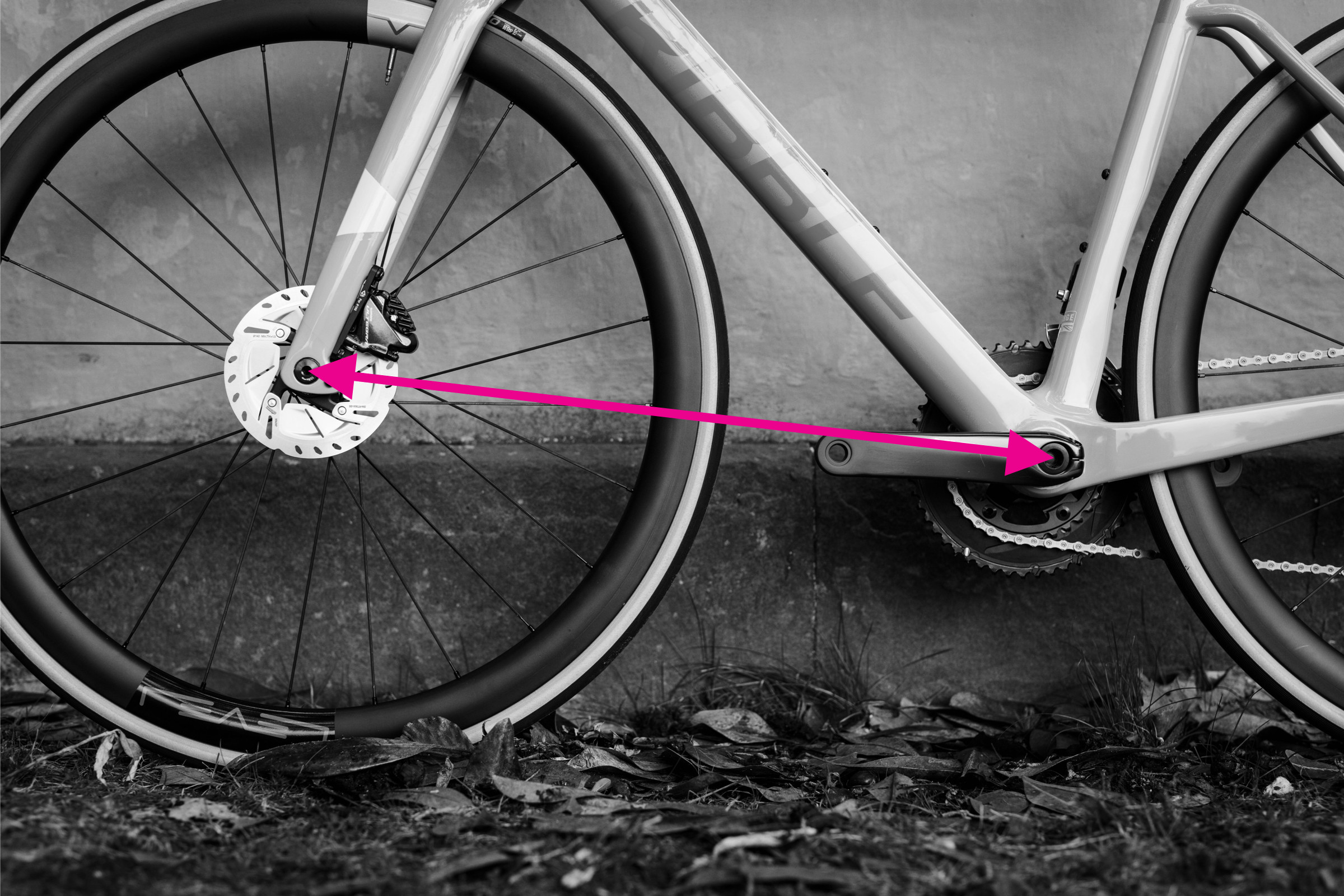 Measuring front center on a bicycle frame
Measuring front center on a bicycle frame
Front center is the counterpart to chainstay length, measured from the bottom bracket to the front axle. It also affects handling and factors into toe overlap.
Steps to Measure Front Center:
- Bottom Bracket Center: Locate the center of the bottom bracket.
- Front Dropout Center: Identify the center of the front axle dropout.
- Straight Line Distance: Measure the straight-line distance between these points.
While front center is less commonly listed in geometry charts compared to chainstay, some manufacturers like BMC include it. It’s important to note that wheelbase is not simply the sum of chainstay and front center because these measurements are not taken horizontally.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Measure Seat Tube and Head Tube Angles
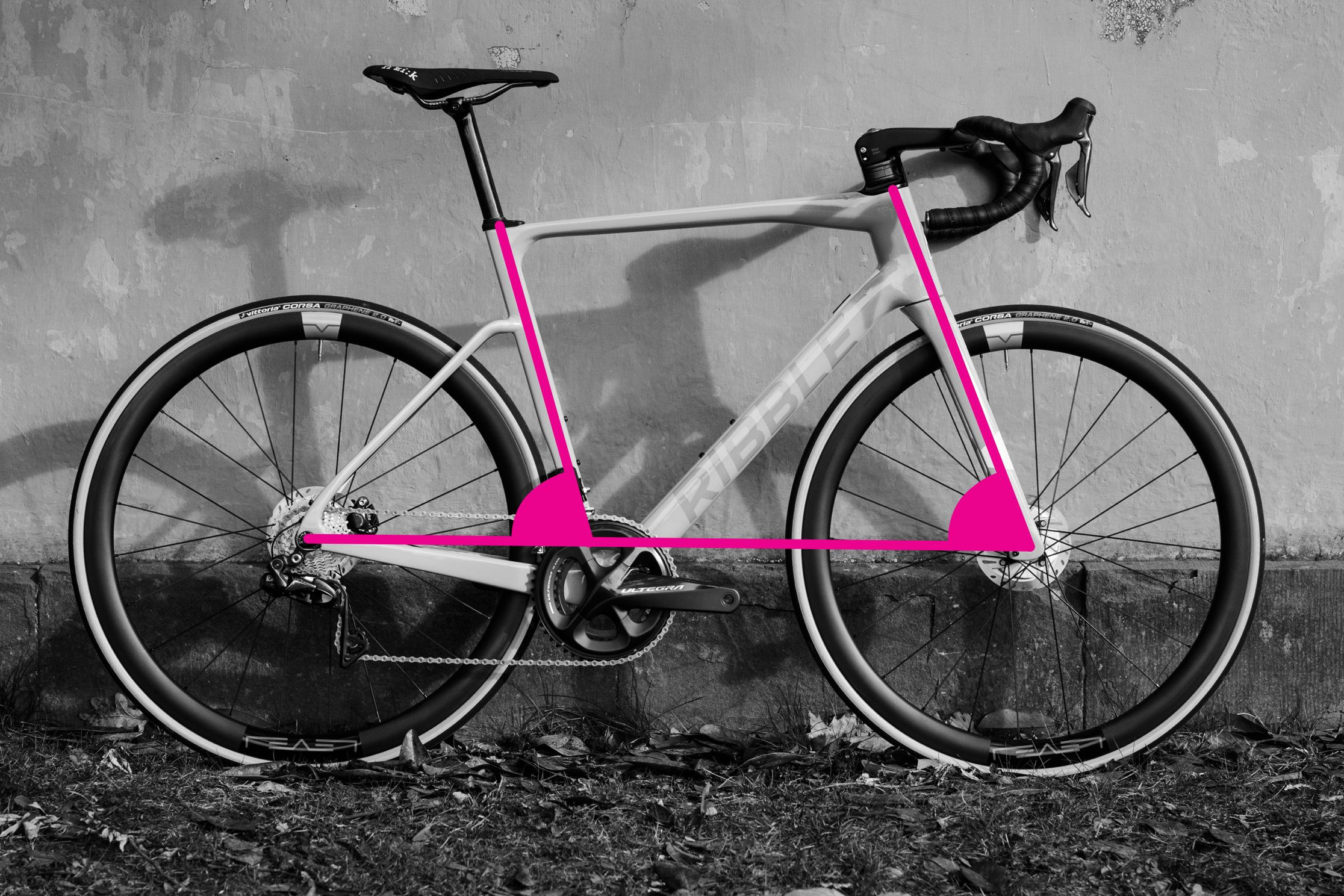 Measuring seat tube and head tube angles on a bicycle frame
Measuring seat tube and head tube angles on a bicycle frame
Seat tube and head tube angles are vital for bike handling. Steeper angles generally lead to quicker, more nimble handling.
Steps to Measure Angles:
Seat Tube Angle:
- Vertical Bike: Ensure the bike is upright on a level surface.
- Clinometer Alignment: Place your clinometer app (or device) along the seat tube. For kinked seat tubes, use a straight edge aligned with the tube between the bottom bracket and seat tube top.
- Read Angle: Read the angle from your clinometer app.
Head Tube Angle:
- Clinometer Alignment: Align your clinometer app with the centerline of the head tube. For tapered head tubes, approximate the centerline or use a straight edge aligning the top and bottom centers of the head tube.
- Read Angle: Read the angle from your clinometer app. Alternatively, on bikes with straight fork legs, you can measure the angle of the fork legs as they often mirror the head tube angle.
Accuracy is best achieved with the bike perfectly vertical. Measuring the steerer tube extension above the head tube can also provide a head tube angle measurement.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Measure Bottom Bracket Drop
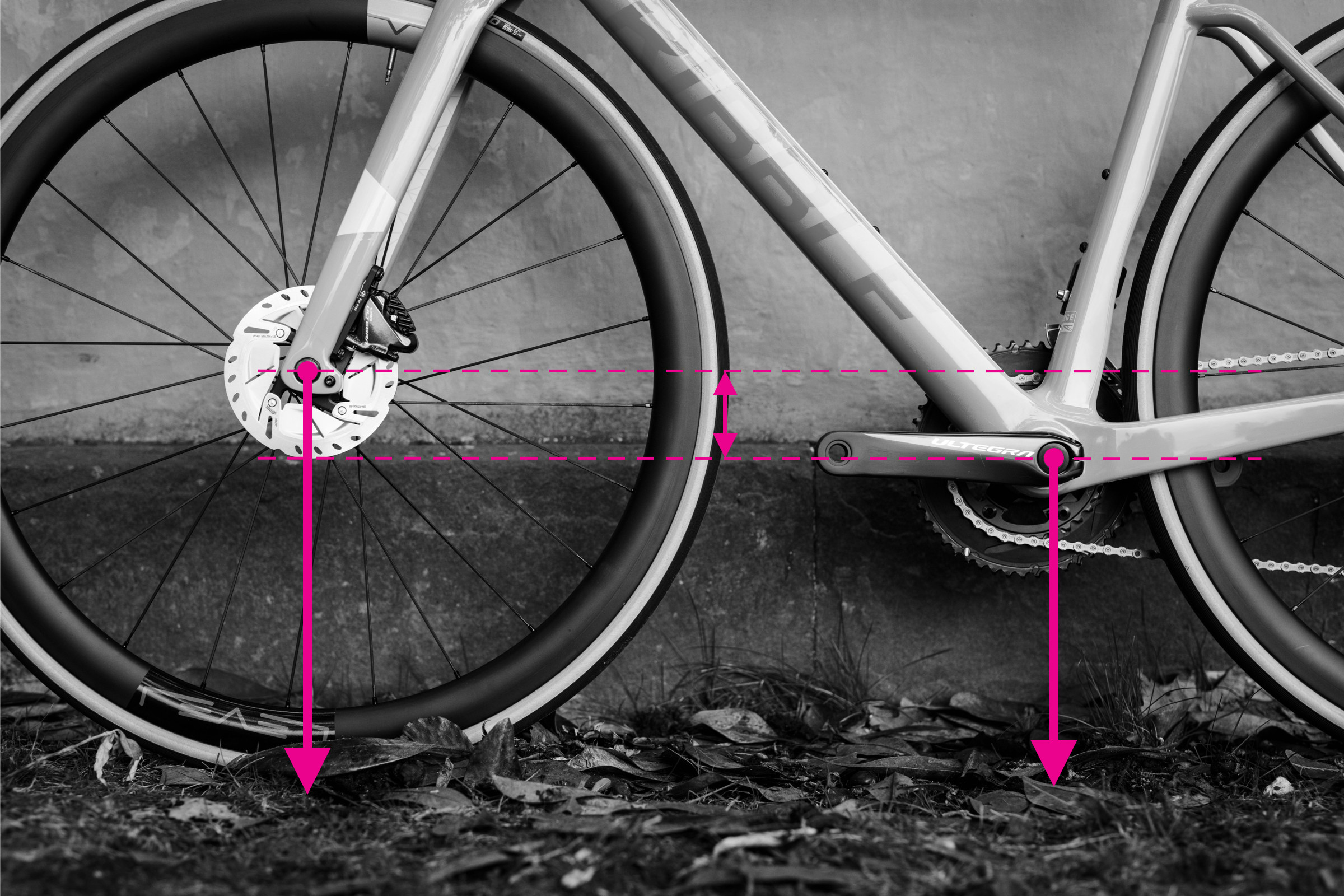 Measuring bottom bracket drop on a bicycle frame
Measuring bottom bracket drop on a bicycle frame
Bottom bracket drop is the vertical distance the bottom bracket sits below the wheel axles. This measurement affects stability and cornering ability.
Steps to Measure Bottom Bracket Drop:
- Rear Axle Height: Measure the height from the ground to the rear axle center.
- Bottom Bracket Height: Measure the height from the ground to the bottom bracket center.
- Calculate Drop: Subtract the bottom bracket height from the rear axle height. This difference is the bottom bracket drop.
This measurement is commonly found in manufacturer geometry charts.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Measure Bottom Bracket Height
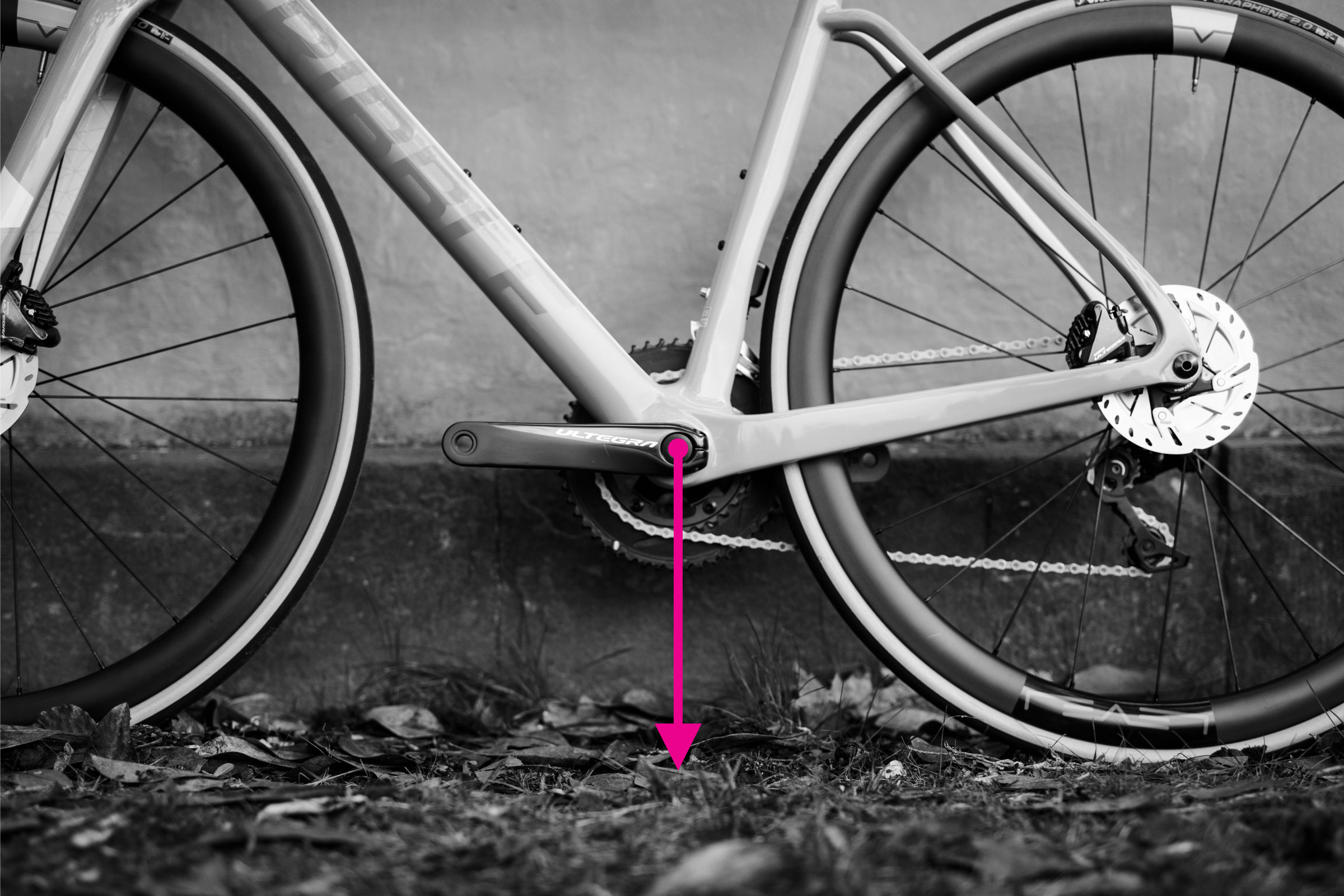 Measuring bottom bracket height on a bicycle frame
Measuring bottom bracket height on a bicycle frame
Bottom bracket height is simply the distance from the ground to the center of the bottom bracket.
Steps to Measure Bottom Bracket Height:
- Vertical Bike: Ensure the bike is upright.
- Measure Height: Measure the vertical distance from the ground to the center of the bottom bracket.
Remember that bottom bracket height can be slightly influenced by tire inflation. Ensure your tires are inflated to your typical riding pressure for the most accurate measurement.
Conclusion: Your Bike Frame Measurement Toolkit
By following this comprehensive guide, you now possess the knowledge and skills to accurately measure a bike frame. These measurements empower you to make informed decisions when purchasing a new or used bike, or when renting a bike for travel or leisure. Understanding these dimensions goes beyond just size labels; it allows you to compare geometries across different brands and models, ensuring you find a bike that truly fits your body and riding style.
Keep your recorded measurements in a safe place. They will be invaluable when you’re ready to upgrade your ride, explore different bike types like road, commuting, or gravel bikes, or simply want to ensure your current bike is perfectly dialed in. Accurate frame measurements are your key to unlocking optimal comfort, performance, and enjoyment in cycling.

